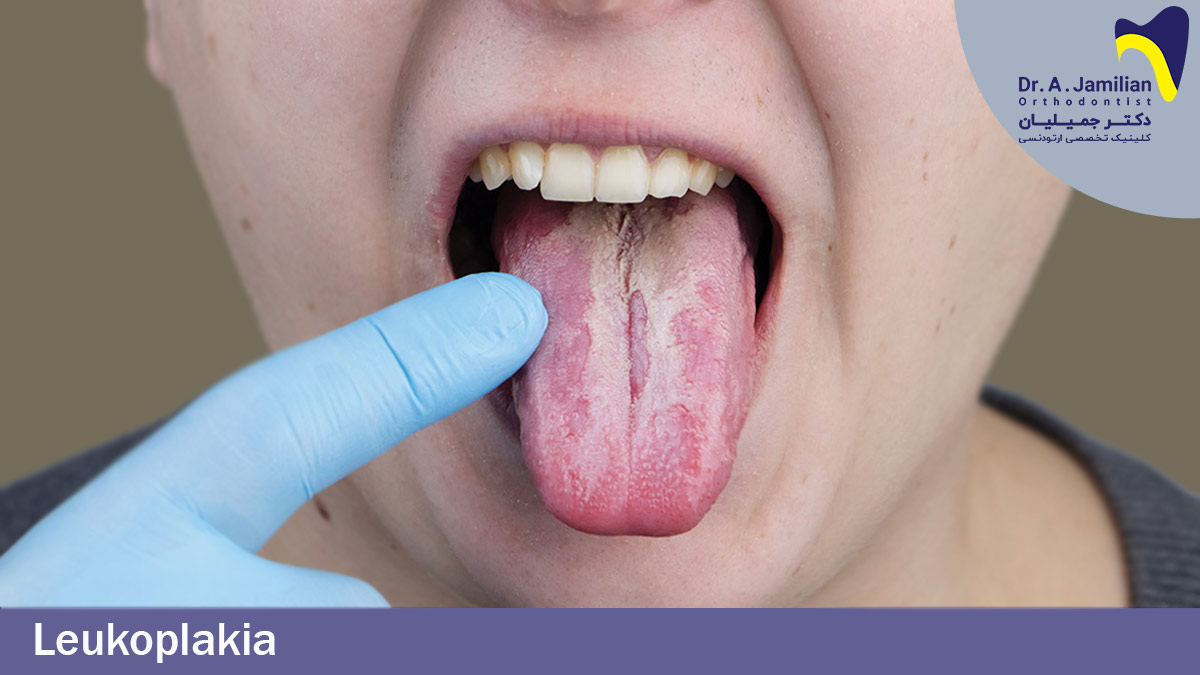
Leukoplakia is the scientific term used to describe the white patches formed inside the mouth, most commonly on the tongue, gums, lips, and other internal areas. Typically, these white patches disappear on their own without the need for treatment. It is important, however, to take more serious measures if the patches do not disappear within one to two weeks, as they can indicate serious diseases such as cancer. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines leukoplakia as “oral white lesions” and highlights that oral white patches do not pose a serious threat to human health. Biopsy and testing are the most effective approaches to accurately diagnose the type of disease. Below, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for leukoplakia.
Symptoms and location of oral white patches (leukoplakia)
Leukoplakia appear as thin white, gray, and sometimes colorless plaque-like patches. Their resemblance to fungal infections often leads to confusion. These spots/patches may develop on all areas of the tongue and mouth, particularly in the cracks of the tongue, and typically do not result in bothering pain or irritation. Some of the most common locations where these white patches may appear are as follows:
- Internal surfaces of cheeks
- Gums
- Beneath the tongue at the end of the oral cavity
- Tongue
- Sometimes, leukoplakia may develop in areas of the body other than the mouth, including the genital area

Causes of leukoplakia
Generally, stress and any other factor that harms oral tissues can be a risk factor for leukoplakia. The most important causes of leukoplakia are as follows:
- Excessive or long-term smoking
- Deficiency of vitamins B and C and even iron deficiency
- Conditions that compromise the immune system, including HIV, chemotherapy, and heavy surgical procedures
- Friction between a broken tooth and the inner wall of the oral cavity
- Severe oral burns resulting from the intake of hot liquids and foods
- Excessive or long-term use of dental abrasives or whitening products
- Loose dentures, orthodontic retainers, and orthodontic brackets with sharp edges
- Prolonged or excessive use of inhalation sprays (e.g., asthma sprays) without rinsing the mouth afterward
- Poor oral hygiene
- Frequent biting or chewing of the inner lining of the mouth or tongue
- Overuse of alcoholic beverages
- Human papillomavirus (HPV), which causes genital herpes
Diagnosis of leukoplakia
As stated earlier, most cases of leukoplakia improve on their own within one to two weeks with no need for medical interventions. However, if after this time, you still notice white spots/patches inside your mouth, it is essential to visit a dentist for diagnosis and treatment. The dentist will review your medical records and perform clinical examinations to first diagnose the cause of these oral white patches and then prescribe the most effective treatment. A biopsy is required for diagnosis. This procedure can be performed in two ways:
- Biopsy using specialized oral brushes that rotate on the lesion to collect the cells
- Excisional biopsy in which the entire lesion is surgically removed
Notably, when leukoplakia is associated with HIV or AIDS, the dentist or physician will prescribe specific antiviral medications in addition to the treatments mentioned above. If precancerous or cancerous cells are identified in the sample, further specialized tests ought to be conducted to assess the severity of the condition. While it is difficult to estimate exactly, approximately 5% of leukoplakia cases may be or become cancerous. As a result, if oral white patches or lesions do not disappear after a while, it is important to consult a dentist to take necessary medical measures.
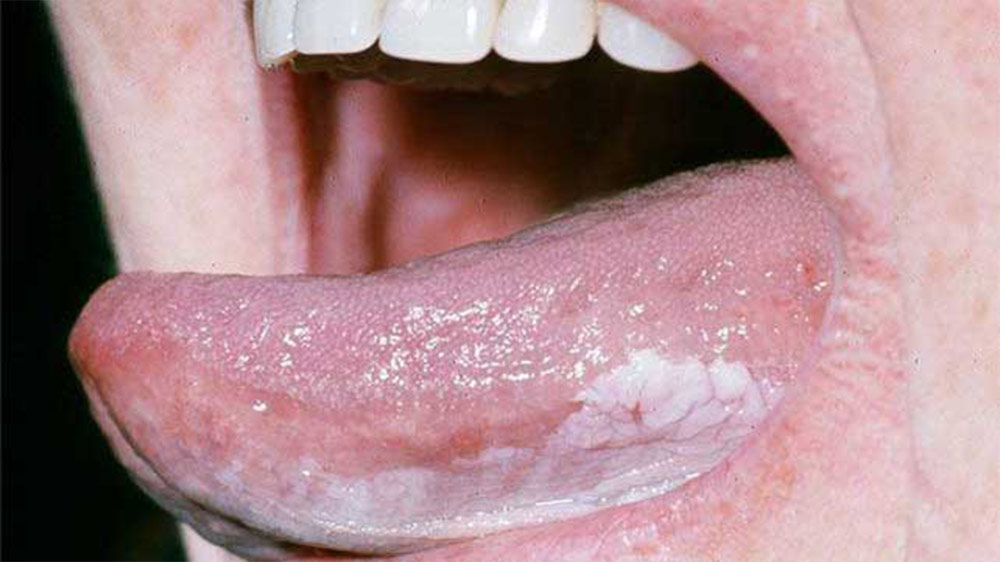
Prevention and treatment of oral white patches or leukoplakia
Practicing good oral hygiene and addressing stressors and other factors that may harm the oral mucosa are the key solutions to prevent leukoplakia. Other recommendations are as follows:
- Cutting down on smoke and alcohol
- Visiting a dentist in the case of bumps on the lips or inside the mouth
- Practicing good oral and dental hygiene
- Gargling with a mixture of water and salt
- Avoiding oral hygiene products that include harsh whiteners or abrasives
- Avoiding loose dentures, brackets with sharp edges, and other similar devices that may lead to chronic irritation of the oral mucosa
- Keeping mouth ulcers clean
- Avoiding hot liquids and foods
- Eating foods that are rich in minerals and vitamins
- Avoiding allergenic and stimulant foods
- Avoiding unconventional, risky, or unprotected sexual behavior
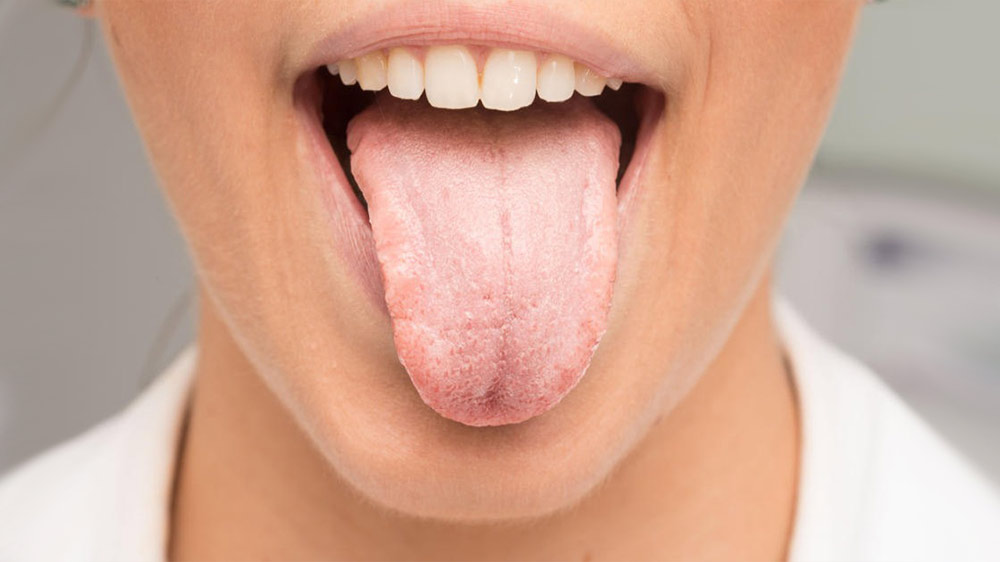

What is the difference between aphthous ulcers and leukoplakia?
In order to understand the difference between aphthous ulcers and leukoplakia, it is better to identify the characteristics of each condition separately. Aphthous ulcers are the most common type of oral ulcers that present as either small or large white lesions. Some ulcers can also present as herpes caused by the herpes simplex virus. These painful mucosal lesions may take about 10 to 14 days to disappear. It is noteworthy that aphthous ulcers are not contagious, but they are typically attributed to genetic factors. Aphthous ulcers can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, immunological issues, smoking, food allergies, biting the inner wall of the cheeks, intake of acidic foods, stress, poor nutrition, or deficiencies in certain vitamins.
Leukoplakia, on the other hand, is characterized by the presence of white and gray patches within the mouth. This type of oral ulcer develops as a result of excessive cell growth. Chronic irritants, such as smoking or drinking alcohol, and other factors previously discussed in this article are the main causes of this condition. It should be noted that most cases of leukoplakia are not cancerous.
What is the difference between oral white pimples and leukoplakia?
Oral white pimples resemble blisters and are typically small, white, or transparent and generally not painful. The development of white pimples can be attributed to several factors, including physical injury to the cheek, obstruction of salivary glands, and dry mouth. Leukoplakia, in contrast, is characterized by the development of white or gray patches or lesions on the inner surface of the cheek and on or beneath the tongue. Leukoplakia is mainly caused by heavy alcohol and tobacco use, mineral deficiencies, poor dental and oral hygiene, and severe oral burns caused by hot liquids.
Prevention and treatment of oral white pimples
Practicing good dental and oral hygiene, maintaining a moist oral environment, and avoiding activities that harm the oral soft tissues are the main ways to avoid oral white pimples. Other preventive measures include gargling lukewarm salt-water solution, practicing good oral and dental hygiene, using mouthwash to prevent infections, brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush, reducing intake of dry, acidic, spicy, and salty foods, and increasing consumption of juicy, soft foods. If oral white pimples persist for an extended period, it is necessary to consult an oral health/dental specialist to determine and prescribe a suitable treatment based on the severity and type of the legion. These pimples may be treated with gels or medications, or the dentist may drain them using a laser.
When should I visit a dentist for leukoplakia?
Many oral white lesions can be eliminated simply by maintaining good oral hygiene and addressing the underlying irritants without the need for specialized treatment. However, legions may prove to be leukoplakia. In this case, they may persist for an extended period and are often associated with other diseases that necessitate medical treatments.
While leukoplakia is not a direct cause of cancer, it elevates the risk of developing cancer. Oral tumors typically develop from severe cases of leukoplakia or those that have been present in the mouth for an extended period. Such cases of leukoplakia may experience precancerous transformations and progressively result in cancer. If you notice any of the following cases, it is necessary to visit a dentist:
- White patches with visible, reddish spots
- White bumps with dark or red spots
- Bumps that are irregular in shape and feel
- Difficulty in eating, swallowing, or moving the jaws
- Oral lesions and ulcers persisting for over two weeks
- Changes in oral tissues
Leukoplakia, which is characterized by white patches in the mouth, may develop due to a variety of reasons. An oral lesion resulting from the patient’s negligence may sometimes be confused with an oral patch or pimple. If you notice patches or pimples inside your mouth, consider whether you have eaten hot or spicy food the previous day. If you have not, it is important to consult an oral health/dental specialist. If your orthodontic appliances have irritated your oral cavity and caused leukoplakia, you need to visit your orthodontist. If you have a broken tooth and it comes into contact with the soft tissues in your mouth, seek dental treatment immediately. Finally, if you suspect that your diet is responsible for leukoplakia, it is better to consult a dietician.