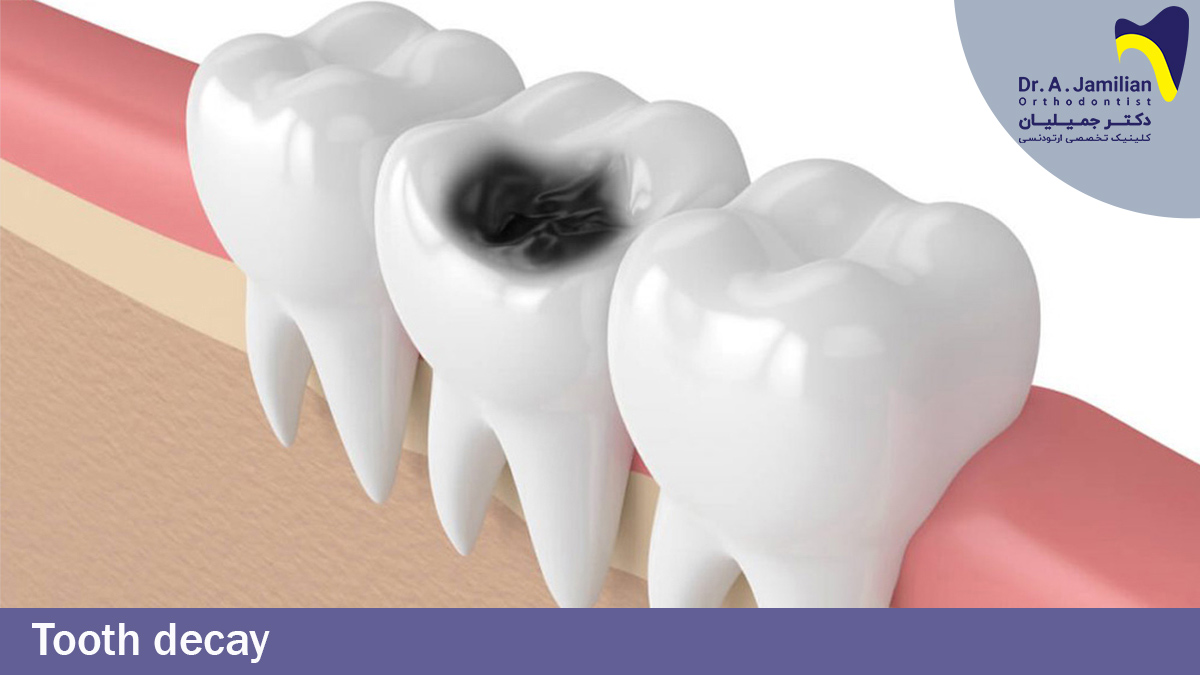
Tooth decay, gingivitis (gum inflammation), and tooth impaction are all amongst the main causes leading to severe toothaches. On top of this, gum recession ,exposure to foods, cold & hot temperatures cause certain symptoms. These include: sensitive teeth, toothache and discomfort. Such symptoms exacerbate the oral inflammation and would hurt the tooth nerves. Thus, the damaged tooth would require denervation therapy. Before experiencing a severe toothache, patients would suffer from certain symptoms such as tooth sensitivity to sweet foods, cold and hot temperature, so upon observing such signs and symptoms they need to visit a dentist.
Actually, tooth decay is the destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth. To initiate decay, the sweet things must be available to microbes, which use the latter to generate the destructive agent of the mineral structures, i.e. acids. For this reason, sweet foods play a key role in the inception of tooth decay. There are certain foods, including snacks, ice-cream, cigarettes, tea, coffee, etc. which can exacerbate tooth decay.
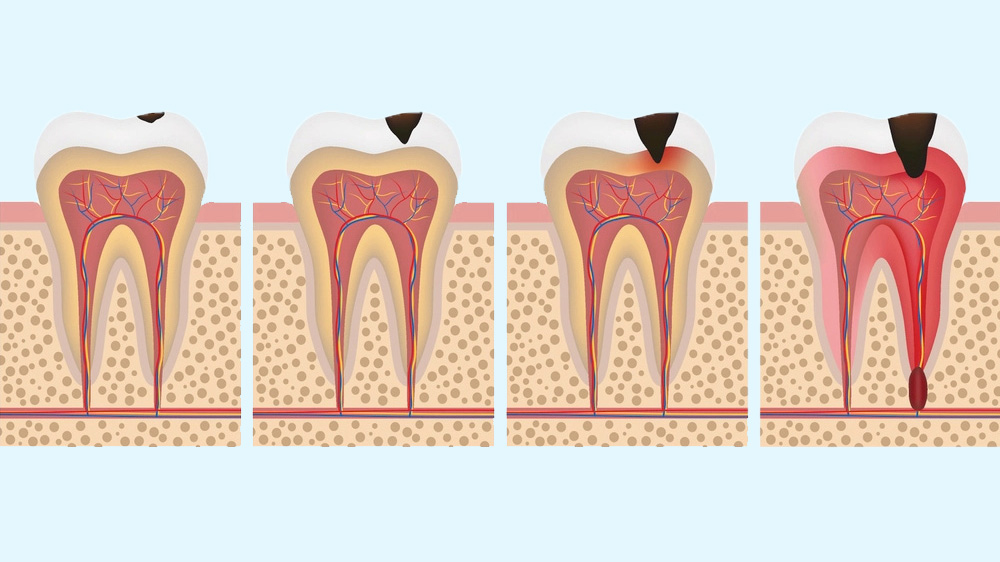
Tooth decay stages
Most patients start to consume painkillers, when they feel a toothache and they stop eating them when their pain is alleviated. You need to know that this temporary relief is not due to the healed disease, but is due to the infection of tooth tissues, veins/arteries and nerves. There is no scientific reason for the exacerbated nocturnal toothaches. In most cases, the severe toothache is a sign demonstrating the tooth decay has progressed and has reached the nerves. In this case, the decayed tooth needs denervation therapy and it would continue until full treatment of the toothache’s main cause.
Common Areas Where Tooth Decay May Be Develop
Decay does not affect all tooth surfaces equally and in a similar fashion. Because of their special status, some tooth surfaces would be affected more than other surfaces. These surfaces are:
1- Fissures of the chewing surfaces
The chewing surfaces of the molar teeth have narrow and deep fissures, which are proper places for microbes to live and grow and also to bring about premature decay of teeth.
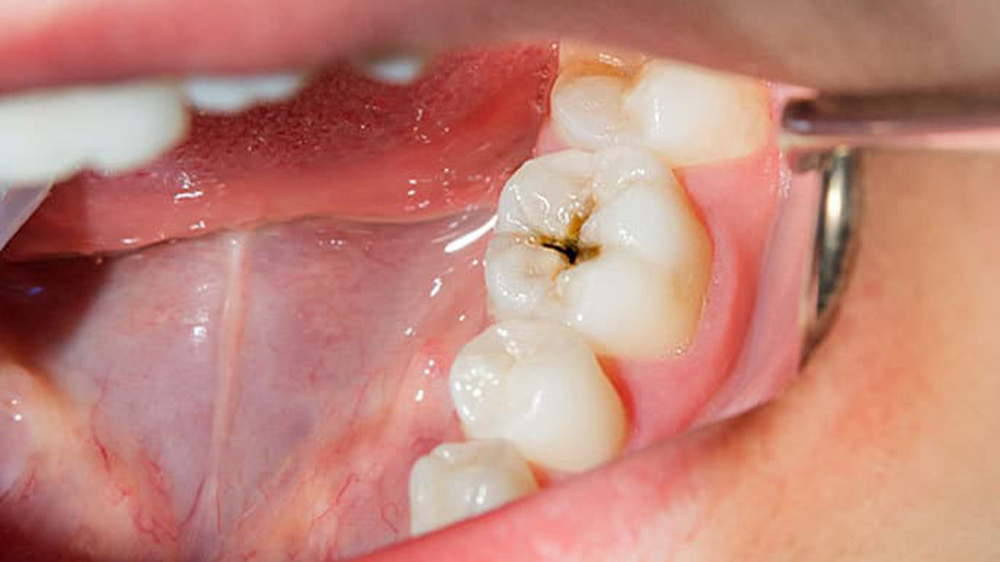
Tooth decay on fissures of the chewing surfaces
2- Interdental Surfaces
Since the toothbrush bristles fail to reach these areas, they cannot be cleaned and brushed, so they are considered as potential places which are susceptible to both tooth decay and gingivitis. The decays one may find across these surfaces are known as the interdental decays.
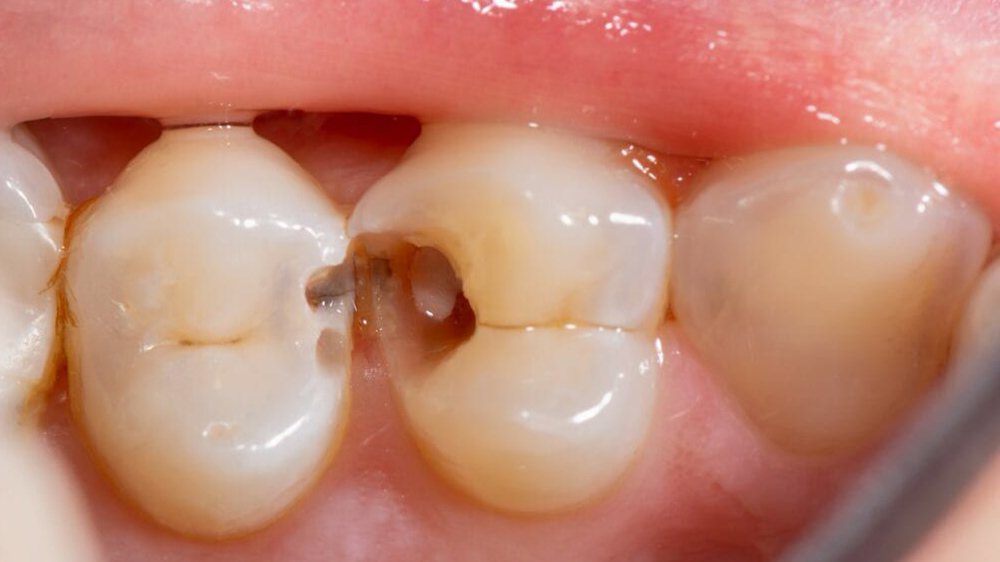
Decay on interdental surfaces
3- Cervix Dentis Or junction Of Gum And Tooth
Cervix dentis or “neck of tooth”, is where the crown and the root of teeth reach each other. The tooth becomes narrower across the cervix dentis. If it is not cleaned well with a toothbrush, the accumulation of microbes may be immense. . It would definitely cause consequences such as tooth decay and gingivitis.
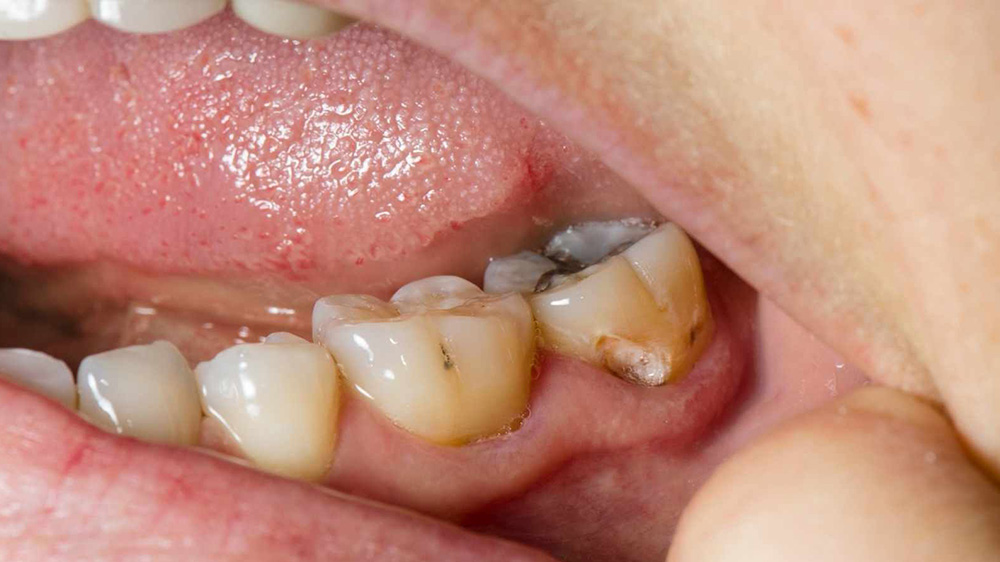
Decay between gums and teeth
Symptoms of Tooth Decay
One or more of following symptoms may be seen when a tooth is decayed:
- Color of tooth’s enamel is changed, as the decayed area of enamel turns brown or black.
- Tooth perforation at the decayed area, sometimes, the destruction is tiny and is diagnosed only through a precise examination; however, sometimes a great part of tooth is removed, as the patient would think their tooth is broken.
- Feeling tooth sensitivity or toothache while eating cold, hot, sour and sweet foods.
- Feeling tooth sensitivity or toothache while we press the teeth together.
- Bad fresh has different causes including tooth decay.
- Tooth decay can cause the foodstuff to get stuck between teeth, which in turn would tear the floss when you are flossing your teeth.
Causes of Tooth Decay
Recognizing the causing factors of each disease is a necessary condition to prevent them. It is the case for tooth decay, so to prevent it, initially we need to identify its causes. Most people who visit dentists usually point to the heritage and type of their teeth in response to why their teeth are decayed? Although it is obvious that the type of teeth is very effective in their durability, there are other factors involved here. Different causes have been identified for the tooth decay, but generally microbes, sugar stuff, tooth resistance and time are among the most important factors causing tooth decay.
These causes always affect the teeth and would bring about tooth decay, as teeth would not decay, if they are absent. There would be no tooth decay without microbes. If there are microbes, but no sweet stuff is present, the decay will be very limited. Both microbes and sweet stuff fail to develop decay in people whose body enjoys a normal resistance against diseases. And finally, microbes, sweet stuff and low somatic resistance would not result in tooth decay in real time, because they need enough time to destroy the hard surface of our teeth.
Microbes Causing Tooth Decay
Naturally different sorts of microbes live in the mouth of human beings, but all oral commensal bacteria do not cause tooth decay. Microbes start to form a layer over the tooth, known as microbial plaque, when it is left unclean for a while. The microbial plaque is a soft and dense layer, consisting of so many different bacteria and oral commensal cells. It sticks to the tooth surface so hard that it cannot be washed only by rinsing. As time passes, more microbes would add to this plaque and would increase its pathogenicity.
It is necessary to point out that the microbial plaque is different from the white soft deposit that sits over the teeth and can be seen without the armed eye. Such white deposits are washed out simply with just water. But the microbial plaque is colorless, cannot be seen easily and is not washed out only with water. The microbial plaque can be seen only when it is dyed with special materials. Some colorful tablets, known as the chewable disclosing plaque tablets are used to diagnose the microbial plaques. To remove the microbial plaques, you need to brush your teeth very carefully and patiently.
Time and Speed of Tooth Decay Formation
Tooth decay is not developed in the blink of an eye, but it takes time for the enamel to be dissolved and the soft tissue of the enamel to disappear. Studies show that after eating it takes 2 to 5 minutes for sweet stuff to reach microbes where the acid is produced. Within only 10 minutes, acid volume reaches its peak and then it remains in that state for another 20 to 60 minutes and finally it gets back to its normal status. After each meal, the microbial plaque environment gets acidic and then after a while it returns to its normal condition. Eating again makes the oral environment acidic. In this way, the teeth in such an acidic environment start decaying. If a kid takes sweet foods 9 times a day, spots will appear on their teeth after a while demonstrating the beginning of the decay process.
Often, tooth decay is a young adults’ disease; this means that in contrast to the teeth of older ages whose presence in the mouth has become longer, teeth are more susceptible to decay when they have grown out recently. Therefore, the importance of caring about the teeth is clear cut in such ages.
Until How Long Can Our Teeth Be Resistant Against Decay?
There are a set of defensive factors in people’s mouths which make the oral environment resistant against decay. Saliva condition. its consisting cells, the teeth form an array, arrangement of teeth, type and all other properties affect somehow the extent to which the teeth would decay. Besides, genetics all fall into place, as some people show more resistance against the destructive factors. The personal resistance would be congenital or acquired. Also, it can be permanent or temporal. However, most authors consider two major factors, microbes, and sweet stuff. Those two are the most important causes of tooth decay. The good news is that there are ways to improve the tooth structure. One of them is to provide teeth with fluoride, as it can enhance / (add onto) the teeth resistance against decay.
Tooth decay commonly occurs in the age ranges of 2-4 years old children. This is due to their use of mothers’ milk or nursing bottles. To prevent tooth decay, you need to clean their teeth after each time they drink their milk.
Causes Of Children’s Premature Tooth Decay
In spite of what most parents believe, iron drops have no effect on tooth decay in their kids, but it just changes the color of the decayed teeth. The most important causes of decays are as follows:
- Leaving the kids’ teeth unclean since the growth of the first baby teeth.
- Improper nourishment pattern including:
- Using the bottle including milk or other sweet drinks as a baby pacifier in order to pacify them and help them to fall asleep.
- Drinking milk from a bottle during night time repeatedly, as the baby wants.
- Decreased saliva flow during sleep.
- Multiple decayed teeth in the mouth of kids’ parents which have not been treated yet.
- Failing to ask a dentist for an examination of the kids’ teeth, and to gather proper information and to conduct preventive tasks since the growth of the first baby teeth.
- Using snacks repeatedly by children, which encourage and stimulate the tooth decay during daytime.
Such factors provide a proper environment for activity of decay-causing microbes in the mouth of children. Generating all sorts of acids, when then becomes the cause for tooth decay.
When Is It Important To Visit A Dentist?
You may not aware of the hole had been developed in your teeth, so, it is important to visit a dentist and ask them to examine your teeth regularly, even when you think that your teeth are normal and healthy, it helps you to heal the decays when they are in their initial stages. If your tooth decay has been progressed and you feel toothache, you need to visit a dentist without any hesitation.
Check-up patient teeth
Treatment of Tooth Decay
To treat the tooth decay, a dentist has to find its main cause. If the decay is superficial it can be treated through filling and veneering procedures. However, if the decay has reached the tooth root, then perhaps denervation therapy and then filing are required. In general, the following treatments are available, out of which the best treatment is recommended by your dentist in terms of severity of your tooth decay and other effective factors.
1- Tooth Decay Treatment with Fluoride
In cases when the tooth enamel is affected very trivially and the developed hole is both shallow and narrow, then the fluoride can repair the tooth enamel. This kind of treatment is carried out using mouthwash and toothpastes containing fluoride.
2- Tooth Filling
The main treatment of tooth decay is filling which is also known as tooth restoration. Dental restorative materials including metallic substances such as amalgam, composite resins with similar color of tooth, porcelain or a mixture of different materials, are used for filling the tooth cavities.
3- Dental Crowns
Dental crowns are used when the case of tooth decay is severe, and the tooth has become feeble. For crowning the teeth, the tooth in question must be casted by the dentist, then based on the developed cast a dental crown made of gold, resin, porcelain mixed with metal or other materials. The crown then is manufactured, and then placed over the specific tooth / teeth.
4- Root Canal Therapy
In cases when the tooth has been damaged severely. and the pulp of the tooth has been involved, root canal therapy is required for the patient. It is clear that after root canal therapy, given the decay & destruction of the tooth crown, the restorative treatments, and methods will be used for either filling or crowning the damaged tooth.
5- Dental Extraction And Implants
In cases when the decay extent is so high that the restoration does not work, at your dentist’s discretion it must be extracted. In such cases, implant therapy can be used after consulting with your dentist.
Tooth Decay FAQ
1- How can we find that we have tooth decay?
Tooth decay usually is diagnosed with the blackened tooth. An exact diagnosis is possible only through regular examination by your dentist. Symptoms of an advanced tooth decay may include sensitivity, feeling pain while eating something, drinking cold or hot or sweet drinks, toothache without obvious reason and toothache while eating foods.
2- Is it possible For tooth decay to be treated naturally?
Tooth decay in it’s preliminary stages may be stopped, and treated. The tooth enamel is able to restore itself using the minerals found in saliva and fluoride gained from the toothpaste and other sources. However, if the process of tooth decay continues, more minerals will be removed. The tooth enamel weakens and eventually disappears over time. As well as, a hole will be developed.
3- What are the main causes of tooth decay?
There are several causes as well as factors for the initiation of tooth decay. Ignoring the oral and dental sanitary instructions is among the most important causes of tooth decay. Other causes are genetics, nourishment and nutrition habits, overconsumption of sweet foodstuff, smoking and having crooked teeth.
4- How long does it take for a cavity in your tooth to convert into decay?
The time for formation of a cavity varies in terms of certain factors including age, type of diet, observing oral sanitary instructions, etc. On average, it would take between six months to four or five years for a cavity to reach a point where it needs treatment.
5- What is the color of tooth decay?
Tooth decay also known as cavity is developed due to acids made by bacteria. The colour all is depending on the type, composition of products developed through reactions of bacteria, cavities’ color varies from white to brown and black.
6- What would happen, if I leave my tooth decay untreated?
Tooth cavity would lead to different consequences such as continuous toothache dental abscess, which in turn would be along with dangerous consequences and septicemia, if it is left untreated.
7- Why is it in some cases the formation of tooth decay is rapid?
The tooth decay is known to commonly when foods containing carbohydrates are stuck between our teeth. ( And we cannot get rid of them only by brushing and flossing ). The major causes of dental decay, cavities are consumption of sweet, sticky foods, and drinks. The more sugar is consumed, the more acid is produced, which then results in tooth decay.
8- Can dental cavities spread to other teeth?
Dental cavities cannot spread into other teeth, but undoubtedly they can affect your other teeth. First of all, the condition in which a cavity is developed on your tooth certainly is able to affect your other teeth as well.
9- What is the best medicine for tooth decay?
Fluoride therapy can help your tooth enamel to restore itself, if the cavity has just started to form, as it can remove a cavity in its initial formation stages. In fluoride therapy, in contrast to what one can find in the drinking water and toothpaste, more fluoride is transferred to your teeth.
10- Is mouthwash useful to get rid of the tooth cavities?
Yes, mouthwash can be used to decrease tooth decay. Also, by fighting against certain conditions such as gingivitis, dry mouth (aka xerostomia) and formation of oral plaques, mouthwash can play a key role in this regard. Mouthwash needs to be used along with toothbrush and dental floss.
11- To avoid tooth decay, what points must be observed while brushing teeth?
A proper type of toothbrush must be used. Maintaining your toothbrush goes along with it, this includes replacing your toothbrush once every two or three months. Ask your dentist, for the the correct way of brushing, and using dental floss is very important in avoiding dental cavities & decay.
12- Will decay of baby teeth affect the permanent teeth?
Short Answer: Yes. The involvement of the permanent teeth depends on both the extent and severity of the baby teeth decay. If the extent of decay is so high that infection can be expected and the tooth buds can be damaged, it may also have adverse effects on adult people’s permanent teeth.