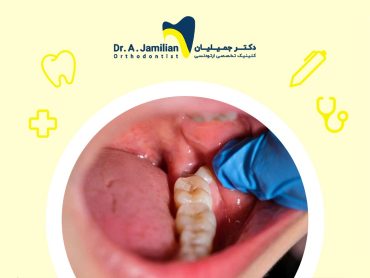
Toothache in children may be felt in or around the tooth like a sharp or radiating pain and can be associated with inflammation or infection symptoms. A toothache may occur due to pressure, heat, cold, or sweets. In severe cases, identification of the tooth problem is often difficult. Children with a toothache should be examined by a specialist to diagnose and treat the problem. If left untreated, toothache usually gets worse. Brushing is typical at this time. However, people in the early 20th century had fewer dental cavities than in the 19th century because fluoride was added to drinking water in the late 19th century in many cities and many dentists began to prescribe fluoride pills as a preventative measure. As a result, dental cavities reduced, and dental health improved, ultimately reducing toothache, especially in children.
Causes of pediatrics toothache
Diagnosing the cause of toothache is the prerequisite of its treatment. Most toothaches in children occur due to one of the following reasons:
- Tooth Decay
- Pulp inflammation
- Abscess
- Gum disease, including periodontitis
- Loosen or broken tooth
- Cracked or damaged tooth
- Unprotected tooth root
- Food left between the teeth or under the gums
- Teeth trauma
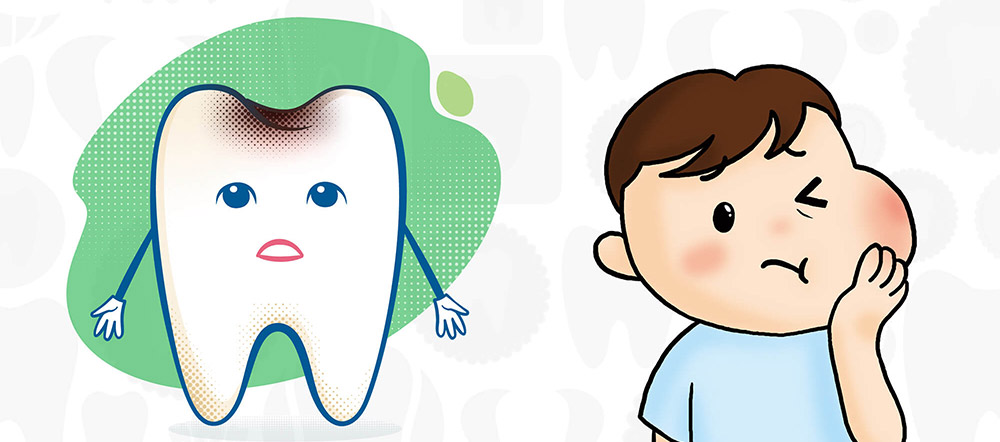
Symptoms of toothache in children
Children cannot complain of toothache; therefore, parents should pay attention to the child’s symptoms and discomfort and the following issues:
- Stimulation of the dental nerve by bending or twisting the teeth (Bruxism)
- Feeling of pain and pressure due to filled sinuses
Toothache prevention in children
Training and institutionalization of good habits in children can prevent toothache, minimize emergency visits to the dentist, and consequently reduce toothache incidence.
- Train to brush twice a day, especially a tooth backside, where cavities usually form.
- As a supplement to brushing, flossing is also recommended once a day.

Toothache relief in children
Toothache in children can be relieved by applying a cold bag or ice wrapped in a wipe on the baby’s jaw.
Avoid hot or cold drink or food and ice cream until pain relief; they may aggravate toothache. Visit a dentist if toothache lasts for more than 24 hours and immediately if the toothache is associated with fever, swelling, severe pain, or bleeding.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If a toothache is due to tooth decay, the dentist will repair the decayed area or the broken part with amalgam or composite. In case of pulp damage, endodontic treatment or denervation will be performed, and the pulp will be removed and covered with a veneer by the dentist. Irreparable damages or severely injured teeth should be extracted. If a toothache is due to an infection, the dentist will prescribe antibiotics.