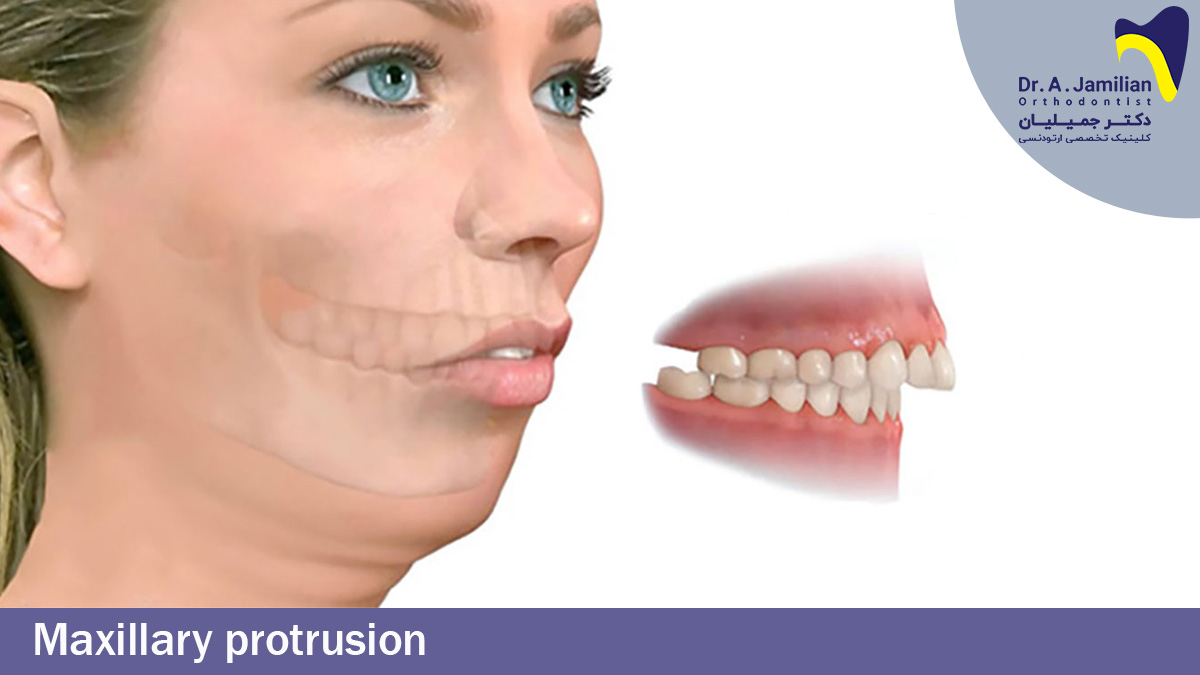
In some cases it is possible that the maxilla is bigger and positioned much forward which in terminology is called maxillary protrusion. In this case in order to realign the maxilla backwards. extraoral appliances such as headgear must be used to prevent the overdevelopment of the maxilla placed on top of head or the nape with the help of bonds. Once the causes of the maxillary protrusion abnormality are recognized, then the orthodontist determines the best method of treatment. The patients who need surgery in addition to orthodontia, get referred to a maxillofacial surgeon by their orthodontist in the most proper time.

Diagnosing maxillary protrusions
Sometimes after observing people with a bigger or much forward maxilla this question may arise: is the maxilla abnormal or is it the mandible that is too small? How does an orthodontist diagnose this?
Normally the maxilla must be a bit more forward than the mandible. Meaning while placing the jaws on each other the maxilla must be positioned 1 to 2 millimeters forward than the mandible. If this measurement and distinction gets larger, then the patient gets diagnosed with maxillary protrusion and prognathism. Thus. This jaw is responsible for the abnormality and is very vital in the proper treatment of maxillary protrusion. The orthodontist can determine the cause of the maxillary protrusion by taking radiography images and analyzing the condition of the both jaws.
After taking the radiography images the orthodontist will begin to examine the numbers and the statistics and make an accurate diagnosis. For instance, the orthodontist considers a number as the norm for the maxilla and if the number obtained from the radiography is higher than the norm, it means that the patient has maxillary protrusion. Also, if the number of the patient’s mandible from radiography is less than the norm, then the patient suffers mandibular deficiency. And this is the reason why the maxilla looks bigger.
In severe abnormalities of maxillary protrusion the patient suffers from abnormalities of the both jaws. Meaning in addition to maxillary protrusion the patient also suffers from the complication of mandibular deficiency as well.
Best treatment for the maxillary protrusion
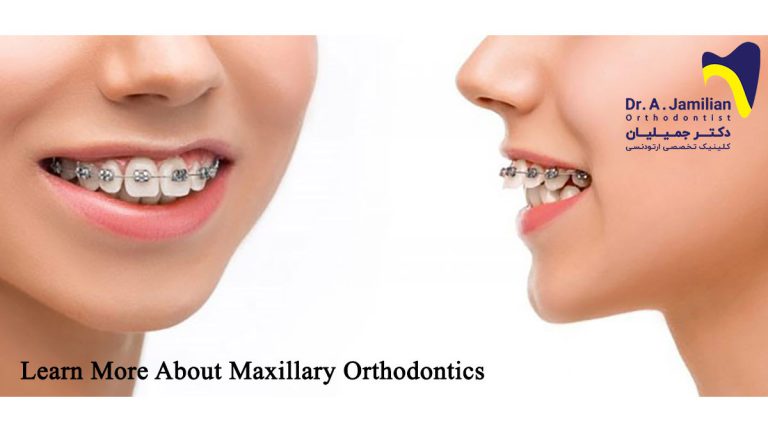
For treating the maxillary protrusion, it is recommended referring to an orthodontist from early ages preferably 8. because the kids’ jaw skeletons are soft and flexible at these ages. Therefore you can get the best results in the shortest time in the treatment of this group of patients. Removable orthodontic appliances can be practical for moving and loosening the jaws.
It is possible that a patient would not have access to an orthodontist in the early ages. Or that the treatment gets delayed due to any other reason. The adults’ maxillary protrusion depending on the orthodontist’s view can get treated only by orthognathic surgery or orthodontics. The orthodontist’s whole effort is to do the treatment only with orthodontia and without surgery.
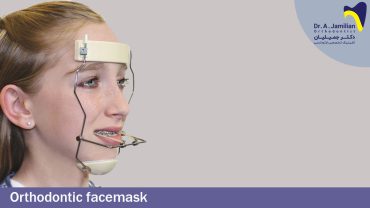
The proper treatment recommended for treating the maxillary protrusion for 1 year olds is removable orthodontics and for 1-1,5 year olds is fixed orthodontia. It is possible that the orthodontist would not have access to small intraoral orthodontic appliances and like old methods he would seek the help of headgears for treating the orthodontic maxillary protrusion.
Headgear types
Two different types of headgear are used depending on the type of anomaly. These appliances are divided into the following types:
- Low pull headgear (cervical headgear)
- High pull headgear (occipital headgear)
- Straight pull headgear
These treatments should be also performed before puberty; otherwise, maxillofacial surgery will be required to retract the maxilla.
Complications of maxillary protrusion
This abnormality causes various complications for the patient that may be a distraction in the patient’s day to day life. These complications are as follows:
- The possibility of intraoral wounds due to the collision of the teeth with the intraoral surface.
- These patients are highly disposed to stroke to the mouth and face because their jaws are way much forward than their face.
- Patients suffering maxillary protrusion have difficulty uttering words and they cannot pronounce the words correctly.
- They usually have difficulty in eating and they cannot chew well.
- Without the proper treatment, the abnormality of maxillary protrusion would develop and get more severe each day.