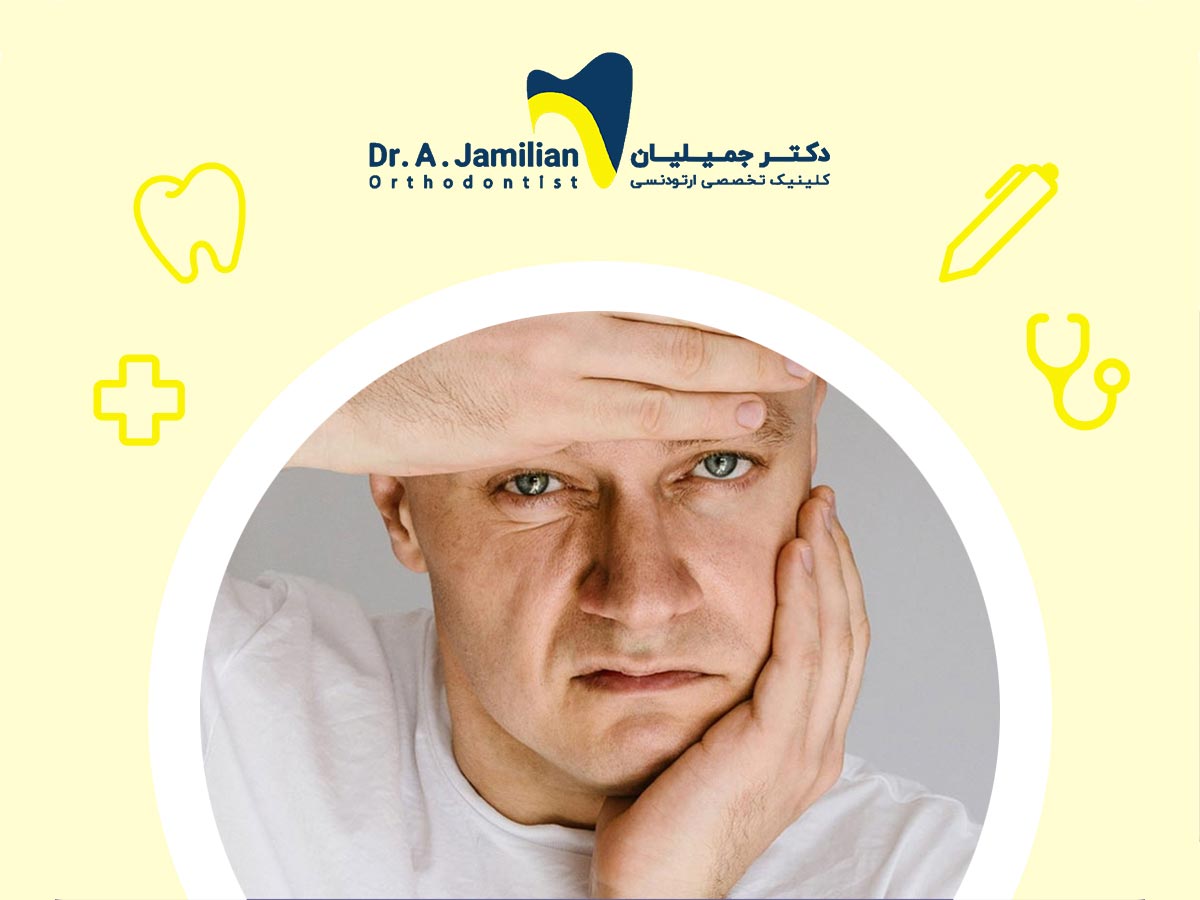
A toothache is a type of warning, indicating a specific issue in the mouth and teeth. Individuals who endure tooth pain for several consecutive days often experience headaches alongside. If you frequently suffer from toothaches or headaches, it is advisable to read this article on Dr. Jamilian’s website and stay informed.
Investigating the relation between toothache and headache
When an individual endures prolonged toothache, they may also experience headaches. The most common causes of this issue are outlined below. We will discuss the detailed causes of each in the following sections.
The relation between toothache and migraine headaches
Toothaches have a variety of factors and effects. The most ordinary are dental decay, impacted wisdom teeth, and more. These specifically, may begin to pave the path towards migraine headaches. Typically, this condition affects only one side of the person’s head, and they may also suffer from nausea and light sensitivity.
According to dental specialists, headaches caused by toothaches are associated with the trigeminal nerve. This cranial nerve, located within the skull, is responsible for controlling senses and movements. Consequently, the upper and lower lips, gums, teeth, head, and face may also be affected, leading to severe pain.
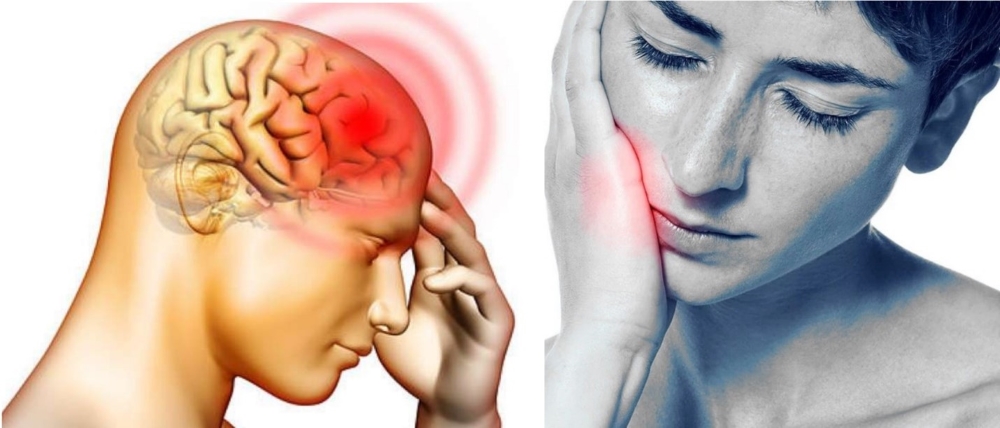
Headaches resulting from advanced tooth decay
Advanced tooth decay and the presence of deep cavities can also lead to headaches. In such conditions, the patient may become uncertain and unable to discern whether the discomfort originates from a toothache or a headache. In most cases, individuals experience such severe headaches that they become unaware of toothache. Since the tooth decay has reached the nerve, it begins to affect other organs, such as the head and ears. Therefore, this headache serves as a form of tension and warning. Individuals should visit a dentist before the toothache affects the head, enabling the dentist to undertake the necessary measures to treat the decayed teeth.
Headaches caused by sinus toothache
It is interesting to know that sinus infections and toothaches are interrelated. A sinus infection can lead to a sinus toothache, resulting in pain in the bones behind the cheeks and the head, making it difficult to bend forward due to increased pain intensity. Therefore, if you suffer from sinusitis, taking precautions to care for your teeth and preventing associated headaches is advisable. The symptoms are as follows:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Nasal congestion with yellow or green mucus
- Ear pain and a sensation of fullness in the ears (aural fullness)
- Breathing difficulties
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is recommended that you visit a dentist promptly for appropriate treatment.
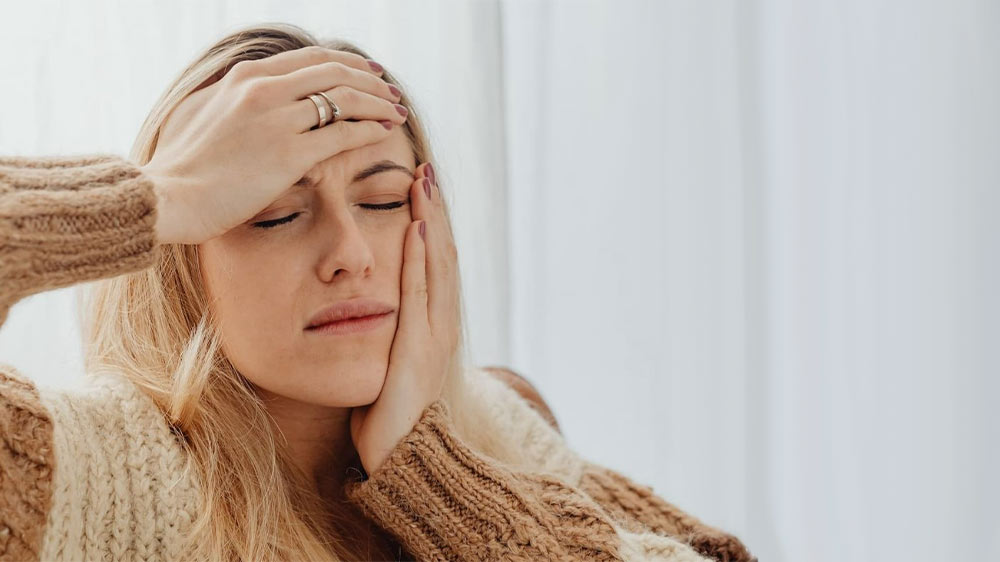

Headaches resulting from bruxism
Habits such as bruxism, or teeth grinding during sleep, can all lead to toothache. Teeth grinding may lead to severe pain in the jaw muscles and head. They may even experience pain in the temple area.
In this article on Dr. Jamilian’s website, we have examined the relationship between toothache and headache. The causes of headaches resulting from toothaches are now clearly understood. The most effective treatment to address this issue is to resolve the underlying dental problems. In most cases, the headaches resolve after the completion of dental treatment. Therefore, taking mild tooth pain seriously and seeking immediate treatment is advisable.
The relationship between toothache and headache FAQ
Yes, headaches can occur due to trigeminal nerve irritation caused by dental infections and decay. In this condition, not only the head but also various parts of the face may experience severe pain..
If you are a teenager experiencing toothaches and headaches, your wisdom teeth are likely erupting. The eruption of wisdom teeth often results in pain in the gums and sometimes in the head.
If dental issues are not treated or pursued, the headaches will persist. In this condition, instead of relying on painkillers, it is crucial to visit a dental clinic promptly for appropriate treatment, which may include addressing an infected tooth or extraction if necessary.