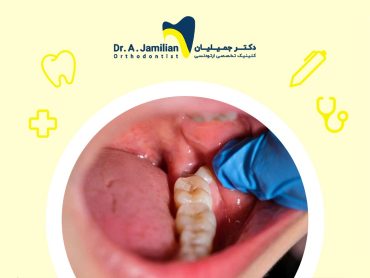
Dental infection begins with a toothache. If a decayed and damaged tooth does not receive a proper treatment, then eventually it will become infected. Untreated dental infections may spread to all parts of the body. This painful problem usually does not occur suddenly but over a long period of time due to lack of negligence and treatment of tooth decay and gum diseases.
If tooth decay is high, the central nerve of the tooth becomes involved over time. And, if the patient is not treated with denervation, the tooth later on becomes infected. Once infection has started, a cyst forms in the root area of the tooth inside the jawbone. In some cases, the cyst was able to be created inside the mouth. opens and the infection develops, and the patient comes to the dentist with a dental abscess and infection and pain. Treatment of this type of complication if the cyst is small. It is a root canal therapy and if the cyst is large, the cyst should be removed with a small surgery performed in the office. In this way, an incision is made on the patient’s gums with a razor blade and access to the end of the tooth root is created. With open surgery, the entire area of the infection is removed and the area is washed with a physiological serum. Then, the gums would be sutured to the bone again.
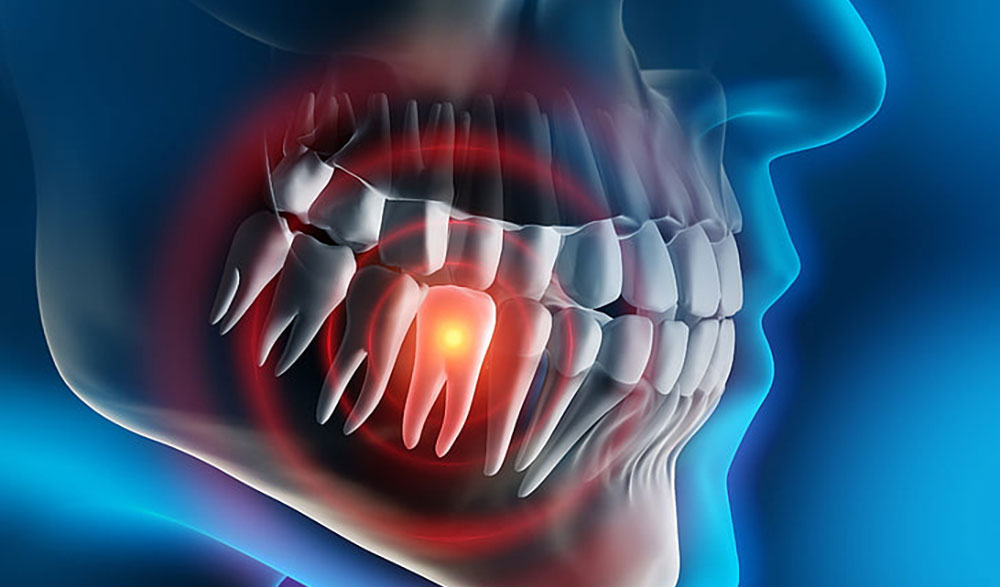
If a patient has throbbing pain in their teeth, there are a variety of issues that may appear. An important one is waking up with throbbing pain in their teeth overnight. In this situation it is possible that the tooth is infected and abscessed, this infection may be able to spread to the near end of the tooth root or around the root. Tooth infection originates from involvement of the pulp and central nerves of the tooth. Often, there is a canal in the center that contains nerves and blood vessels, (collectively called the pulp). If it develops and approaches the dental pulp, bacteria and germs, it will invade and multiply in the pulp. As the microorganisms multiply, the infection spreads into the pulp cavity, by spreading the infection to the end of the root. The infection can penetrate into the tissues adjacent to the root and into the bone.
In other words, tooth decay is able to cause the destruction of tooth enamel and damage to the softer layer of tissue under the tooth, namely dentin. On top of this, it can enter the center of the tooth, which includes the tooth pulp, (called the inflamed pulp). In this way, the tooth pulp dies and becomes infected. Microorganisms continue to infect the pulp until the infection spreads to nearby tissues as well as to the bone that surrounds the tooth, causing a tooth infection.
A tooth / teeth infection is a collection of dead white blood cells, residual tissue, and microorganisms. The source of tooth infection varies much from gum infection. Infection, abscess of the tooth or periapical infection originates from the central canal of the tooth. Or, the pulp of the tooth forms at the end of the root of the tooth. However, abscesses and gingival or periodontal infections occur when an infectious cyst forms outside the tooth and near the root. The type of treatment for a gum or tooth infection depends on the source of the infection.
Symptoms of Dental Infection
Infected teeth may have one or all of the following symptoms:
- Toothache
- Feeling pain in the jaw, ear or neck (usually on the same side of the toothache)
- Toothache that increases when sleeping
- Sensitivity to pressure in the mouth
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks
- Inflammation of the cheek
- Swelling of the lymph nodes, tonsils and neck
- Fever
- Smelly breath
- Feeling an unpleasant taste in the mouth
If the dental infection isn’t cured and spreads to other parts of the body, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Feeling unwell and extremely tired as well as having a headache
- Fever with red skin, sweating or chills
- The face is so puffed-up that you cannot open your mouth completely. Breathing and swallowing saliva will be very hard.
- Increased heart beat leading to an increased heart pulse and headaches.
- Breathing rate exceeds 25 times per minute.
- Nausea and diarrhea
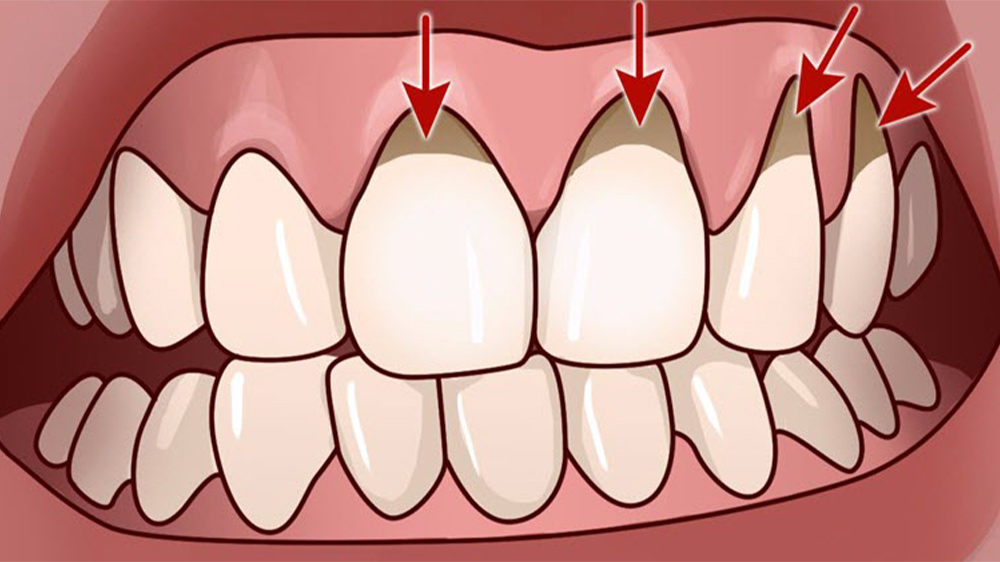
How does a tooth get infected?
The bacteria that enter a tooth through a crack or decay can lead to a tooth infection. Risk factors for dental infection include:
- Poor oral and dental health due to not brushing twice a day and not using dental floss.
- A diet which contains so much sugar, like having a lot of sweets, chocolate and carbonated beverages.
- Dry mouth which is usually caused by aging, various diseases or breathing constantly through the mouth.
Preventing dental infection
If you do not follow the tips related to oral and dental health, you are at risk of tooth infection. So pay attention to the following recommendations:
- Brush your teeth with a fluoride toothpaste at least twice a day.
- Use a dental floss at least once a day
- Cut down on the sugar in your diet.
- Plan and follow a proper diet that includes high amounts of fruits and vegetables.
- Avoid tobacco and its derivatives.
- Drink fluoride-containing drinking water.
- Have regular dental visits.
Treating dental infection
In order to treat dental infection correctly, it’s important to head to a dentist immediately. It is suggested to use water and salt solution frequently before visiting. Patients can also use an analgesic to relieve your toothache at night until they can see a dentist.
The dentist will properly examine and the type of infection will be determined. Sometimes, a dental x-ray is recommended to diagnose a dental infection accurately.
The next step is to have the infection drained and emptied. On top of this, the dentist will prescribe an appropriate antibiotic for you. In most cases, a secondary treatment such as endodontics is required. To prevent dental infection from returning, it is suggested to treat any dental decay and fracture. Hence, do the procedure of treating your dental infection completely in order to make sure it’s complete removal.
In some cases, the root of the tooth is completely destroyed due to chronic infection and it is impossible to repair and maintain the tooth. In these cases, the dentist extracts the tooth and empties the infection completely.
Common questions regarding dental infections
1-Are turmeric and thyme suitable in treating dental infections?
The antimicrobial properties of turmeric and thyme have been proven in the past. However, no scientific research has been published regarding the effects of these spices being effective in treating dental infection. Thus, don’t waste time treating a dental infection with these spices and see a dentist immediately.
2-What should we do with the infection of a tooth that has already undergone a root canal treatment?
You will suffer from dental infection in cases you have not taken good care of the dressing of a tooth with a root canal treatment, or have delayed in visiting a dentist in order to have the tooth restored and the dressing removed. In these cases, the dentist has to first treat the infection and then start repairing your tooth. Therefore, the process of treatment and restoration of such teeth is done with postponement.
3-How are the home remedies for treating dental infection?
Home remedies of dental infection are a temporary way to relieve pain and infection until you see a dentist. In the meantime, you can use a solution of water, salt and ice packs. It is recommended to dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a cup of water and gargle it and then take it out of the mouth.
4-Is treating dental infection an emergency?
If dental infection is not treated on time, the risk of damages in the tooth root and losing a natural tooth are more. Also, the pain of an infected tooth is very severe and will disturb the patient’s life and comfort. Treatment and taking care of dental infection should be done immediately and without delay.