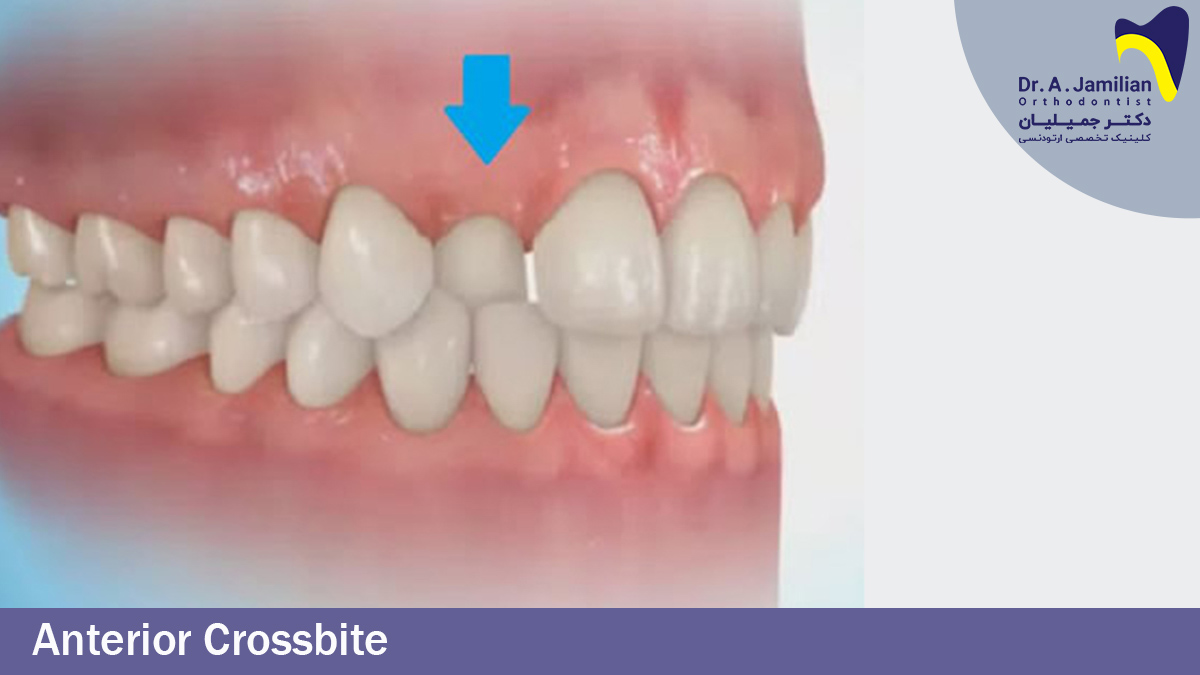
In most scenarios, maxillary teeth are 2 mm ahead of the mandibular teeth. However, if not anterior cross bite will occur in which the lower teeth are ahead of the upper teeth. This type of Crossbite should be treated as soon as possible. Otherwise it will result in protrusion of the mandible, leading to Class III skeletal malformations due to mandibular growth.
This disorder is easily treated with a removable plaque if treated at an early age. Anterior cross bite should be treated upon observation otherwise it will lead to the Class III skeletal malocclusion requiring jaw surgery at the age of 18. Prevalence of Crossbite malocclusion in children is around 4% to 5% which is classified into two types of Crossbite; posterior crossbite and anterior crossbite. Here, we will elaborate on the anterior crossbite malocclusion.
The anterior crossbite malocclusion is important to be treated as soon as possible in the early ages, since in the older ages (18 years old). This is due to the completion of the development of teeth, the mandible is placed in front of the maxilla which leads to Skeletal Class III malocclusion (skeletal cl lll).
Various Types of Anterior Crossbite Malocclusion
Dental: One or two teeth and their jawbone will be affected in a crossbite malocclusion. Sometimes crossbite is able to involve multiple front teeth causing the mandible to protrude and maxilla to sit back.
The anterior crossbite is a type of the dental crossbite malocclusion that could be diagnosed during childhood between the ages of 6 to 7 by examination. . Because the patients are not fully grown yet, dental development is not completed and orthodontists will be able to control the development of teeth in maxilla and mandible by orthodontics appliances. This allows treatment for this malocclusion much easier at a young age. But, if the patient reaches the age of 15 and puberty occurs, the treatment will be difficult. This is due to the jaw being completely developed and orthodontics treatment is not possible per se. The ortho-surgery is used for these cases.
The anterior crossbite malocclusions could be caused as a result of mandible problems. In these cases, all front teeth are involved in this type of malocclusion. The anterior dental crossbites affect the child’s beauty and results in temporomandibular joint problems, long-term pain in both jaws, and teeth erosion.
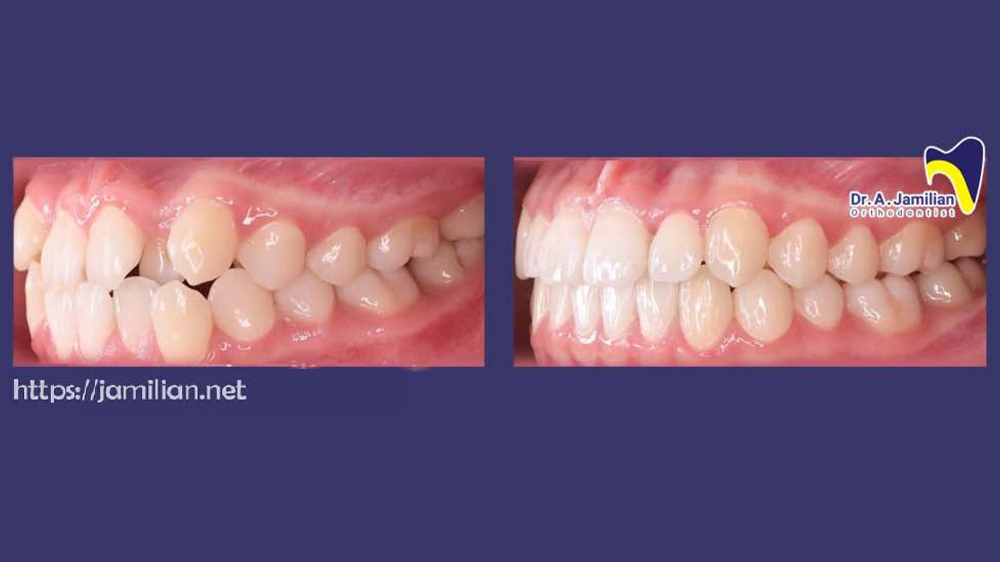
Factors Causing Anterior Dental Crossbite
Anterior dental crossbite occurs due to the following reasons:
- Excessive number of teeth could cause teeth crowding and misalignment of the front teeth, which results in protrusion of the teeth in the lower jaw.
- The Lingual placement of teeth buds in the upper jaw
- Side effects of palate treatment surgery and left lip that hinders the development of the dental arch.
- Crowded Teeth.
- Over-retention of deciduous or temporary teeth.
- Genetic effects.
Side effects of anterior crossbite
The most common side effects of anterior cross-bite abnormalities are as following:
- Class III Skeletal abnormality
- Tooth breakage due to improper contact of teeth
- Enamel loss due to wear of teeth
- Muscle contraction and headaches due to pain and constant pressure on the teeth for a long time
- Inability to speak and pronounce multiple words correctly
- Difficulty during chewing and swallowing
- Adverse effects of Temporomandibular joint and jaw and Mandibular deviation.

Treatment of anterior teeth crossbite
This dental malocclusion can be easily treated by visiting an orthodontist in childhood by the following ways:
- Removal of malpositioned primary teeth for proper growth of maxillary and mandibular teeth.
- Using a removable orthodontic appliance in the mouth.
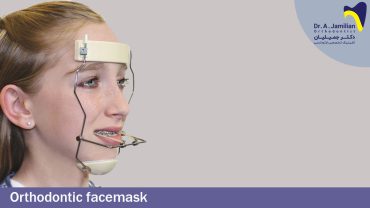
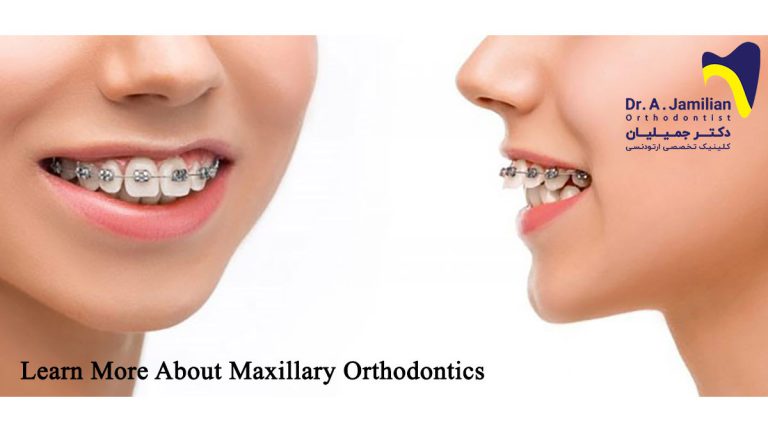
There are two treatment plans after 12 years of age
The first choice is to move the teeth in the right direction using fixed orthodontics
The second choice is orthognathic surgery, which is used after the age of 18 and when the growth of the two jaws has stopped. This treatment plan is used in severe cases.