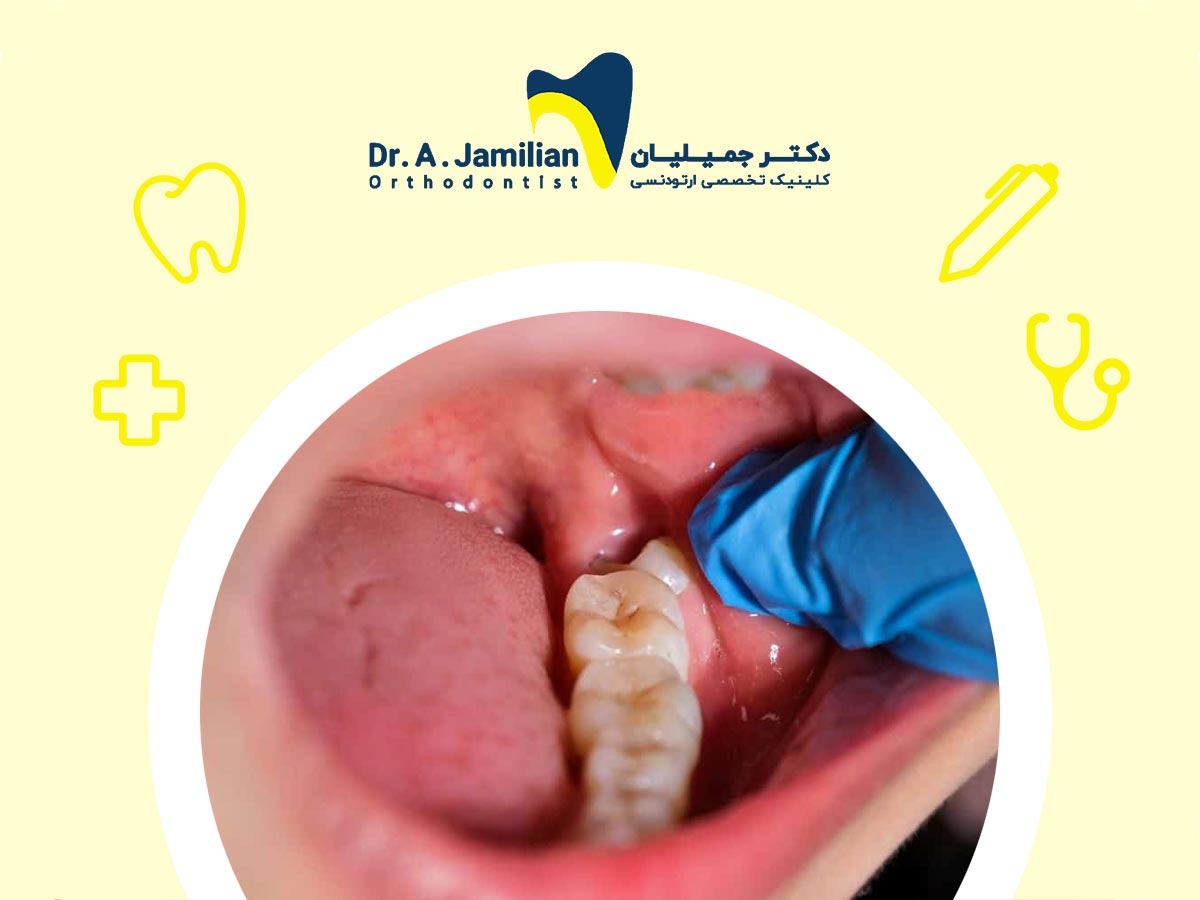
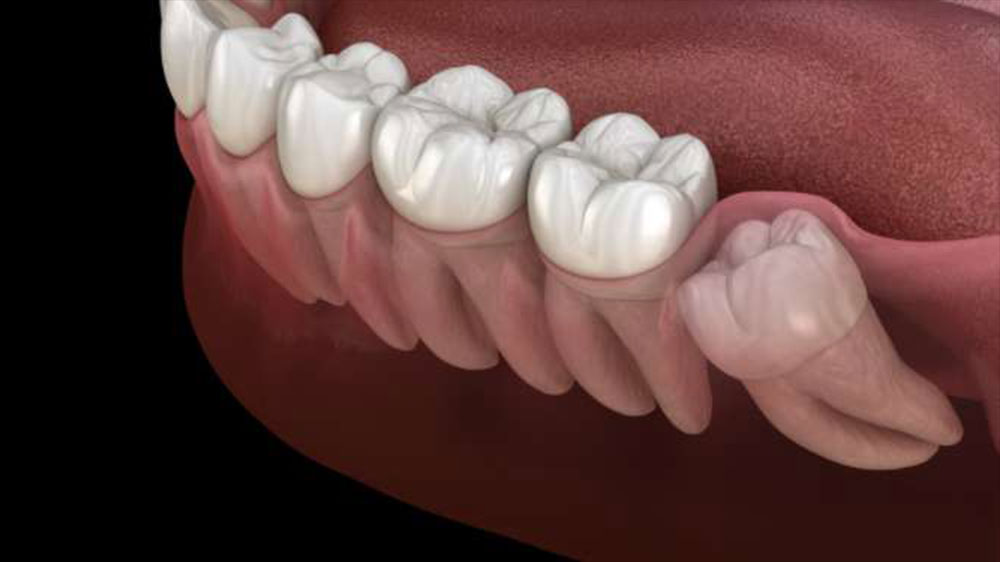
The last teeth to erupt, wisdom teeth, occasionally fail to emerge and end up fully under the gum. When this happens, it is called an impacted wisdom tooth. People with soft gums and ample jaw space are less likely to experience impacted wisdom tooth problems. This guide explores the types of impacted wisdom teeth, their symptoms, treatment options, and associated risks.
Types of impacted wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth commonly begin to emerge between the ages of 15 and 25. If wisdom teeth cannot fully emerge due to lack of room, they become impacted or partially impacted. This condition is more common among people with smaller jaws and firmer gums. Impacted wisdom teeth vary in growth direction and patterns. The most common types are described below. Understanding these patterns can help you determine the condition of your impacted wisdom tooth.
| Type of Impaction | Description |
|---|---|
| Bony Impaction | The tooth is visible and partially embedded in the jawbone |
| Mesial Impaction | دThe tooth is angled toward the front of the mouth. |
| Vertical Impaction | The tooth grows straight but lacks room to fully emerge. |
| Horizontal Impaction | دThe tooth grows sideways and horizontally. |
| Distal Impaction | The tooth is angled toward the back of the mouth. |
| Soft Tissue Impaction | The tooth is partially trapped in the soft gum tissue and is partially impacted. |
Symptoms of an impacted wisdom tooth?
If identified early, the treatment becomes significantly more manageable. Common symptoms include:
- Intense pain at the back of the gums
- Redness and swelling at the back of the gums
- Bad breath
- Ear pain
- Gum bleeding in certain cases
- Pain near the temporomandibular (jaw) joint
- Swelling near the tooth’s eruption site
If you experience some of these symptoms, you may have an impacted or partially impacted wisdom tooth and should consider prompt evaluation for potential extraction.
Treatment for an impacted wisdom tooth
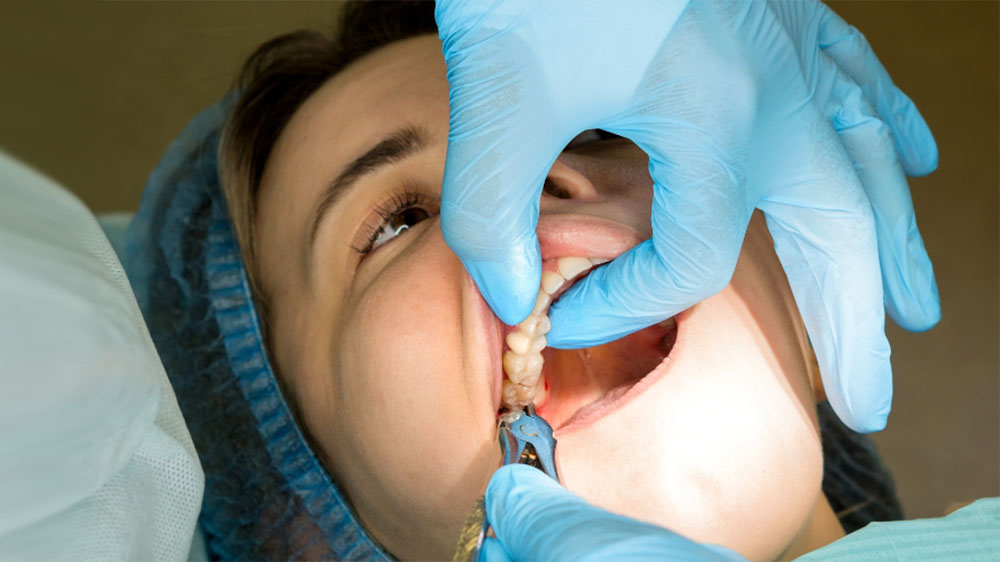
The only treatment for impacted or partially impacted wisdom teeth is extraction. These teeth don’t aid in chewing. Moreover, brushing and flossing are often impractical because the teeth can be hard or impossible to reach. Unfortunately, this may lead to decay in the impacted and nearby teeth. Therefore, extraction is usually the best solution.
Wisdom tooth removal is commonly performed once the teeth have fully developed, typically before age 30, although the timing varies for each individual. A specialist will determine the best time for extraction for the client.
The procedure is generally done under highly effective anesthesia to prevent pain. The dentist makes an incision in the gum, often removing the tooth in sections for easier extraction. Importantly, one should follow post-surgical care instructions for proper healing. For more information, see Wisdom Tooth Removal and Pain.
Risks of not removing an impacted wisdom tooth?
Neglecting an impacted wisdom tooth can lead to complications for the patient. Therefore, it is best to take the surgical treatment of impacted wisdom teeth seriously. In the article The Right Time to Remove a Wisdom Tooth, we discuss in detail the appropriate timing for wisdom tooth extraction. If you have an impacted wisdom tooth, be sure to read the mentioned article. Leaving an impacted wisdom tooth untreated can lead to:
- Damage to neighboring teeth
- Increased risk of gum disease
- Higher likelihood of cyst formation in the gums
- Headaches and dizziness
Risks of wisdom tooth surgery on impacted teeth near the nerve?
The surgery becomes riskier when the nerve is close to or entangled in the root. Complications could include temporary or permanent numbness in the lips, chin, or neck. To minimize potential damage, the surgery shall be performed by a specialist. To reduce risks, a technique called coronectomy is occasionally used, where only part of the wisdom tooth is removed. If the nerve proximity is too great, the dentist may advise against extraction and leave the impacted wisdom tooth as it is. Therefore, it is crucial to determine the type and position of the impaction accurately.
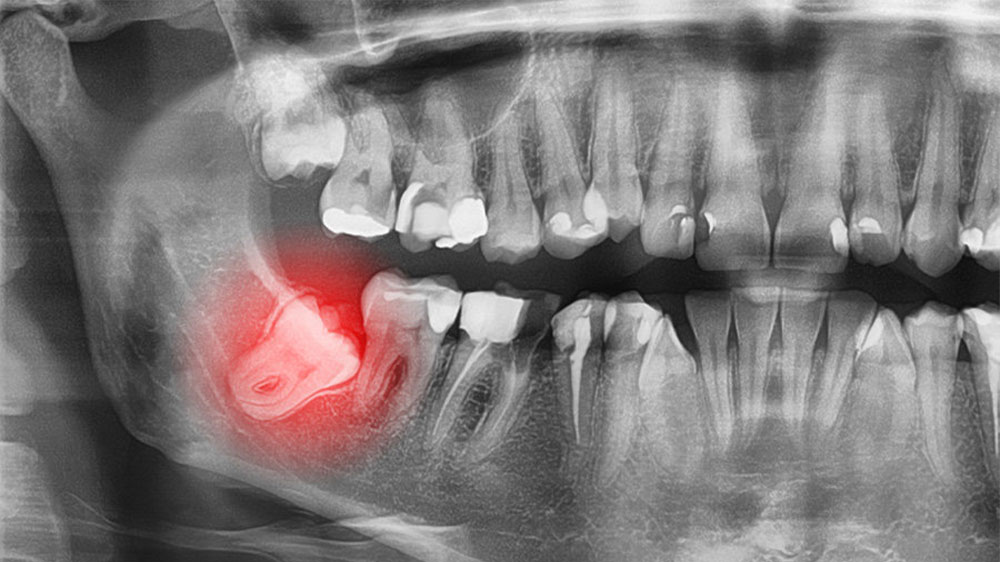
Risks of an impacted wisdom tooth near the sinus?
A further problem with impacted wisdom teeth is their closeness to the sinuses. This isn’t always the case, as it depends on your unique jaw structure and oral conditions. The proximity of the root of the upper wisdom tooth to the sinus can lead to additional pressure on the sinuses, potentially causing sinus infections. Symptoms of increased sinus involvement may include pain, congestion, sinus headaches, fever, mucus discharge, and allergic symptoms. In such cases, extraction is usually recommended.
In this article, we discussed what to do about impacted wisdom teeth and the various growth patterns of impacted teeth. Now that you’re familiar with the complications of this issue, it’s best to seek treatment from a specialist as soon as possible.
In this article, we discussed what to do about impacted wisdom teeth and the various growth patterns of impacted teeth. Now that you’re familiar with the complications of this issue, it’s best to seek treatment from a specialist as soon as possible.
FAQs about Impacted Wisdom Teeth
The most common symptoms of an impacted wisdom tooth are severe pain and discomfort in the back of the gums, especially when chewing food. Other symptoms may include redness and swelling of the gums, visible gum bulging at the tooth’s eruption site, gum bleeding, and swelling in the jaw and face. A radiograph will provide a definitive diagnosis.
Yes, a growing impacted wisdom tooth often causes pain.
There is no specific age for wisdom tooth extraction, as the timing depends on each patient’s condition. However, dentists typically recommend removing impacted wisdom teeth in the late teens or early twenties. It’s best to proceed with extraction before symptoms like pain, swelling, or gum bleeding develop.