Teeth breaking is a phenomenon that occurs due to unpleasant incidents and may happen to everyone and the lack of knowledge about the cautionary actions in specific circumstances can lead to fragmentation, cracking, and breaking. In some cases, teeth breaking is painless and it doesn’t cause more than beauty and health issues. In other cases, due to the pain that the broken tooth causes, the restoration of the broken tooth is counted as a medical urgency and it needs attention and instant treatment.
Familiarity with the structure of healthy teeth
To get a better understanding of the outcomes of broken teeth, we have to analyze the reasons that lead to this case. Originally, a tooth is made of 3 layers of enamel, dentin, and the tooth pulp. The outer layer is called enamel which is the hardest substance in the human’s body and it’s even harder than the skeletal bones that form your skeleton. The enamel is white and it’s the visible protective layer around the teeth. The part of the teeth which is placed above the gingiva (the gums) and shows itself when we smile, is called tooth dentin. There is a soft tissue (called dentin) beneath the tooth enamel that forms the major part of the tooth structure and plays a protective role for the tooth pulp which contains blood vessels and nerves. Actually, the dentin and the pulp hold the tooth roots firmly in the jaw. The lower part of the tooth contains tooth roots which are placed in the gum and the jaw and they’re not covered by the enamel, however, they are covered by another layer which is called the cementum. Cementum is like the tooth enamel except it’s softer. The superficial layer is the tooth enamel which is more in danger of getting damaged and broken.
When a tooth shrinks, cracks, or breaks, at first it will affect the outer layer (tooth enamel). Nevertheless, in specific circumstances, damaging and breaking may involve the dentin and dental pulp. For instance, the face and teeth may take damage in an accident. In normal situations, the inner layers of teeth are not involved in breaking. However, if the broken teeth restoration isn’t done in time, dental pulp and dentin may be stimulated or infected.
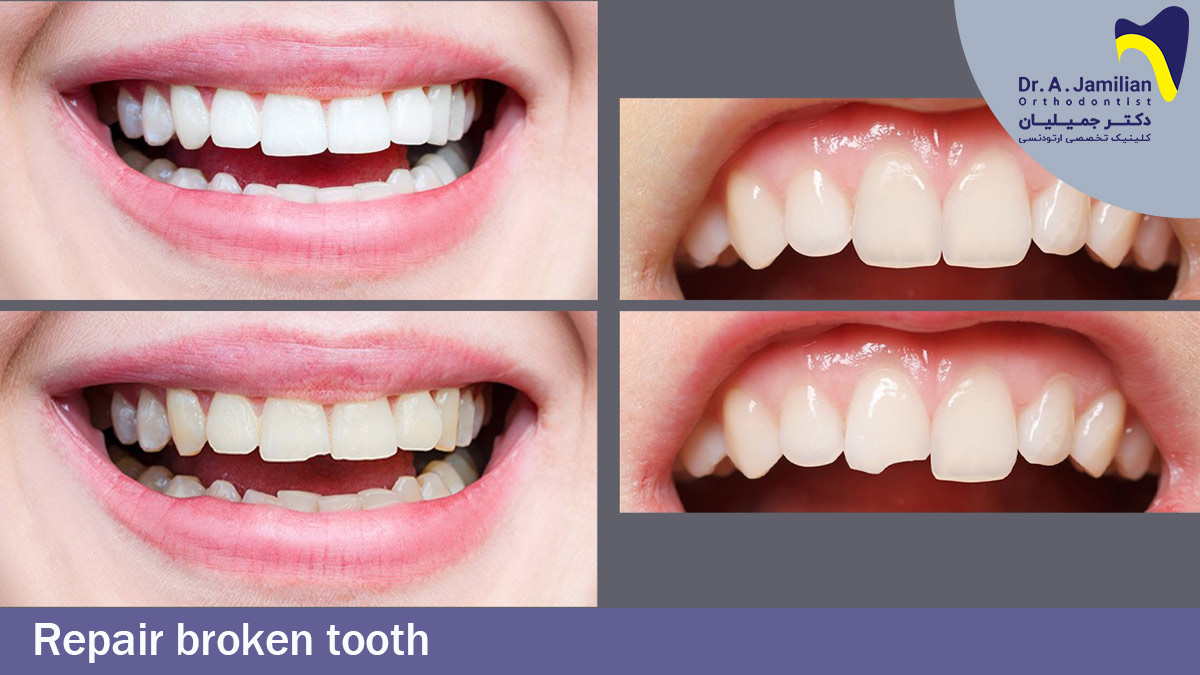
Repair broken teeth methods
The recommended treatment-related methods and the best method of restoration are dependent on the cause, the damage rate, and the tooth decay. Here, we explain some methods that dentists use for broken tooth restoration.
Repair broken teeth methods: tooth contouring
If the breakage is minor and small, the restoration process will contain rounding and shaping the sharp edges of the teeth, and polishing and shaving it in a way that it becomes a match with other teeth, and the breakage manifests itself naturally in terms of beauty.
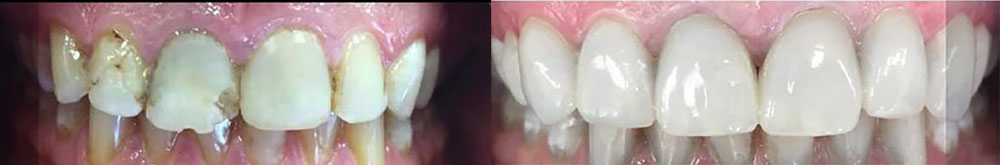
Repair broken teeth methods: the dental filling
In this method of restoration, the special dentistry materials are used and placed in the broken or cracked point. These materials can be Amalgam, Composite, Glass ionomer, etc. Then the dentist shapes them to make them aligned with other teeth and the materials will tighten and harden in order to make the restored teeth look natural.
Repair broken teeth methods: dental crown
Dental crowning is one of the broken teeth restoration methods that is commonly used for each patient. This method exclusively helps patient’s replace the crown with the broken part of the tooth. In this case, the basal parts and the major structure of the teeth will remain healthy. Additionally, an artificial dental crown is made completely or slightly. Right after, it will be attached to the tooth to make it more stable and to keep the natural teeth as much as possible. The root canal treatment often is required to ensure success in broken teeth restoration.
Repair broken teeth methods: root canal treatment
For more damages, in times that the inner structure of the teeth (the pulp) is damaged, the natural dental root can be rescued by cleaning and filling. By keeping the tooth’s natural root, the crown, and the enamel of the tooth will be totally weakened and will require artificial crown installation.
The final way in the restoration of a broken tooth: dental extraction
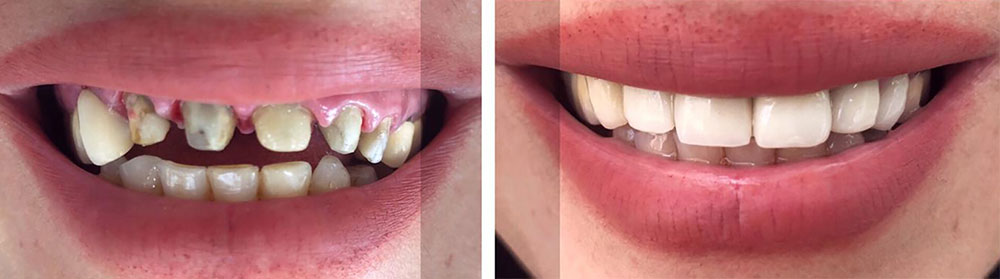
For severely damaged teeth, the previous methods will have no hope in restoration The last remaining option for the patient will be dental extraction. Dental extraction will cause a gap and split between the teeth. In order to maintain gums health, smile beauty, and increase your self-confidence, a need for denture is often felt. In such cases, dental implant methods are used for broken tooth restoration.
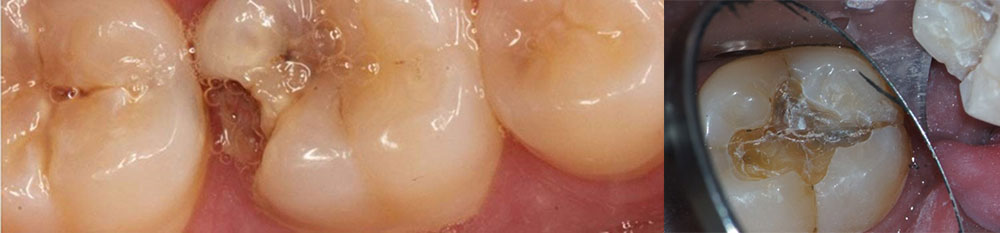
Repair Broken Teeth FAQ
If your whole tooth is broken but the tooth roots remain safe, wash your mouth with water immediately and put the broken tooth in a tiny bowl filled with milk, water, or serum. If bleeding is also involved, stop the bleeding by putting pressure. If the bleeding is too serious, call an emergency.
If your broken tooth causes sharp irritating edges and leads to a tongue wound, you can cover it with a piece of gum, gas, or wax. If you feel too much pain, take a painkiller, or use a cold compress to reduce the pain.
Unlike the skeletal bones of our body, the teeth can’t restore themselves when they receive damage. In these cases, medical actions are recommended for restoration.
In some cases, tooth breakage and cracking are insignificant in a way that the person doesn’t realize it and it will be diagnosed only by imaging. In such cases, no danger threatens the patient. However, if the breakage becomes clear and left with no treatment, it may cause serious damage to the tooth roots by tooth decay.
If the broken tooth is left untreated, the possibility of bacteria entering the tooth root, where the nerves and blood vessels are, will be facilitated. Once infections reach the tooth nerve parts, the patient will suffer toothaches and severe tooth sensitivity.