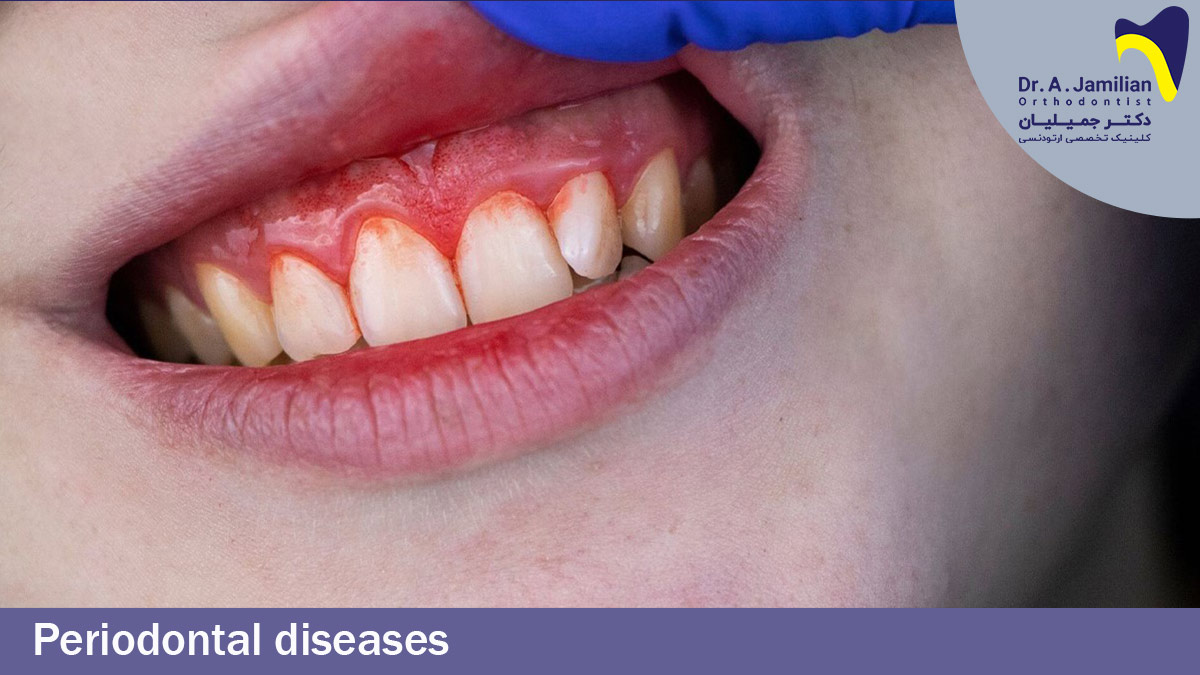
As time passes, periodontitis separates the gum from the teeth and creates a distance between them. Plaques form in the dentogingival junction and weaken the bones around the tooth. Periodontitis is a common disease, and many people in its early stages can be treated with correct oral and dental care, but ignoring periodontitis can cause jawbone recession and teeth loss .A diseased gum, however, is red, loose, and bleeds easily, such that the blood may spill on the pillow while sleeping. Sometimes the gum is inflamed and creates a bad mouth odor.
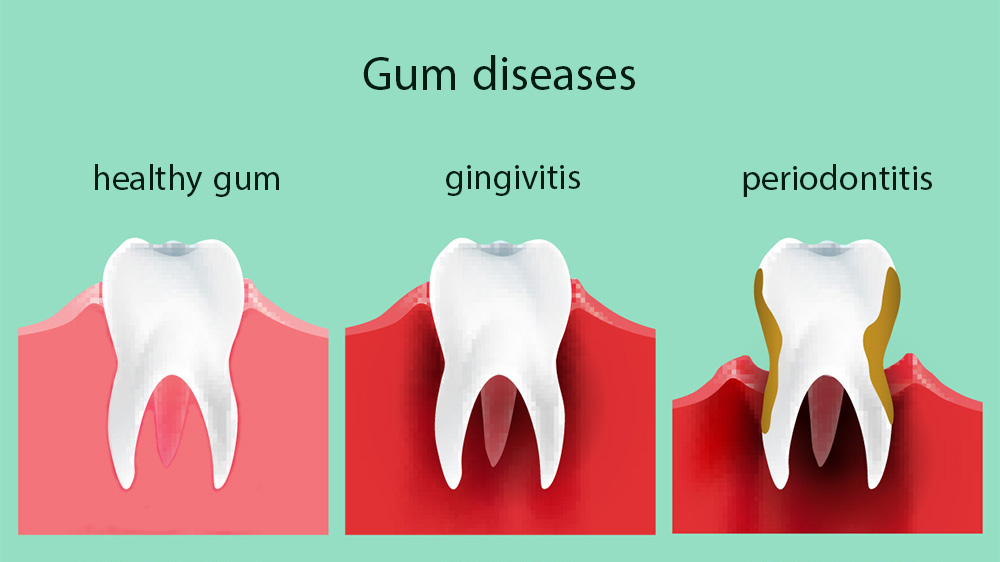
Characteristics of A Healthy Gum
A healthy gum is pink, strong, thin, has acanthi matching the edges of teeth, and a gum surface with an orange skin and a scabrous condition. Gums are made of soft tissues that surround the ends of teeth (dental roots). Taking care of gums is as important as taking care of teeth. Periodontitis is an infection that causes microbial plaque, which is the adhesive layer that accumulates on the teeth and gums.
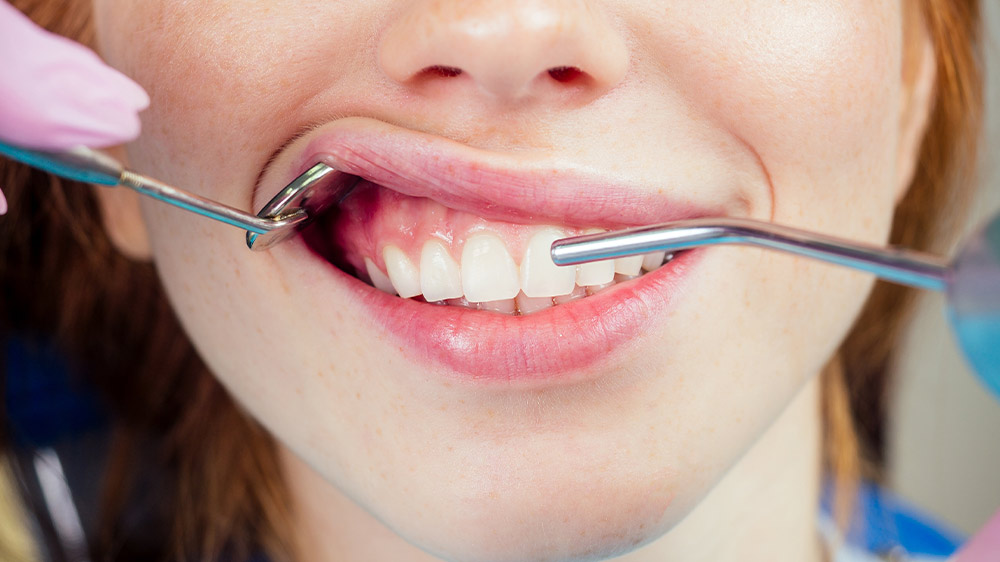
Bleeding Gums
Gingivitis and bleeding can be symptoms of a periodontal disease that leads to the loss of the holding bone in its advancement, causes teeth loosening, and finally, teeth loss. While biting hard fruits, brushing, constant bad mouth odor, loosening of one or multiple teeth, gingival recession, and interdental spaces gum disease causes gum redness and inflammation. Visit a dentist to implement their recommendation about oral and dental hygiene.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is treatable with simple therapies such as dental scaling and improved oral hygiene. The inflammation and infection that spreads beyond the gum and permeates into deeper tissues around the teeth is called periodontal disease and is followed by the loss of bones around the teeth, causing loose teeth.
Various Periodontal Disease Types
Periodontal disease is often caused in acute (invasive) and chronic types. Chronic periodontal disease often affects the youth around puberty and 20 years of age. There is not much dental germ and plaque in these patients, but the decaying is high, which is mostly caused by genetic and immunologic factors. The second type of periodontal disease is chronic, often occurs after 30 years of age, and its most important cause is germ accumulation and bacterial plaque. Microbial plaque accumulation is caused by not brushing and flossing or brushing incorrectly, which is why dentists recommend regular examinations and scaling.
The Risks of Delaying Periodontal Disease Treatment
Delaying periodontal disease treatment causes the bones and tissues holding teeth to be affected, and causes loose teeth as well as toothache in some cases.
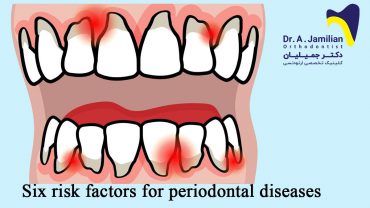
Factors Causing Periodontal Disease
Additionally, along with microbial plaques & not observing health principles, there are other ways to weaken the body’s immune system. More specifically, a food regime lacking nutritional foods and vitamins a, c, and e, folates, beta-carotenes, and minerals can weaken the body’s immune system and may cause periodontal disease. Furthermore, psychological, mental stress and smoking also weakens the body against periodontal disease. A small fun fact for periodontal disease is that illnesses such as diabetes can intensify it.All of these together create a traumatic experience for any patient, and it is important to contact your dentist as soon as possible.
Smokers are 3 times as likely to suffer from advanced periodontal disease, and smoking delays wound healing after gingival and oral surgeries. Cigarettes cause a brown to bitumen color sedimentation, change the color of teeth structure, and increase plaque formations on the teeth and caries.
Periodontal Disease, the Cause of Many Other Dangerous Diseases
Periodontal disease and microbial plaques are risk factors for heart disease patients who suffer from vascular congestion. Research shows that periodontal disease makes vascular congestions twice as likely.
The more severe the gingivitis, the higher the number of bacteria entering the bloodstream, and the higher the atherosclerosis risk, where blood vessels become thicker and thicker and disrupt the blood supply. These people are more susceptible to heart attacks and strokes.
Gum Surgery
In gum surgery, the gums are pushed aside after anesthesia, and then sutured back in place. However, they bring it lower after cleaning the infected tissues and correcting the jawbone. A special dressing is then placed on top, and the sutures are removed 7 to 10 days later.
After Gum Surgery
Pain, inflammation and minor bleeding are natural after gum surgery and disappear in 3 or 4 days. However, if they continue out of that range, and intensifies contact a dentist.
It’s better to avoid consuming cold and hot liquids, brushing the area, and using mouthwash on the first day after gum surgery, but it’s unproblematic on the second day.
The teeth become hypersensitive to thermal simulations such as cold and heat due to gingival recession and cervical and root exposure after gum surgery. The regenerated dentin is formed and dental hypersensitivity is gradually reduced after 4 weeks, but anti-hypersensitivity toothpaste is used if this trend continues. Pregnant women suffer from gingival enlargement and gingivitis (as explained in the pregnancy section) due to hormonal changes, and gingivitis also occurs as a side-effect of certain drugs. There is a 50% gingival enlargement in epilepsy patients. Antiepileptic drugs have a chemical structure for increasing the number and size of gingival blood vessels and fibroblast followed by higher fibro collagen production, resulting in further enlargement and inflammation. Such patients are asked to better observe oral hygiene, and the doctor can prescribe similar drugs to prevent more gingival enlargement.
Here are some of the symptoms of periodontitis
Gingivitis: Gums that are red or swollen that bleed while brushing and using dental floss have the initial symptoms of gum disease and can be treated by observing correct oral hygiene.
Toothache or hypersensitivity: The gum’s removal from the tooth surface causes hypersensitivity when eating or drinking hot or cold foods and liquids.
Halitosis: While biting, those suffering from jawbone recession may pull their teeth from the root. This is the most advanced stage of gum disease, classified as “chronic periodontal disease”.
Important points for preventing periodontal are as follows:
Brush your teeth and gums. Use dental floss to clean interdental spaces. Don’t forget the back of the teeth, as more plaque gathers in these areas due to inaccessibility.
Change your toothbrush once every 3 months, since old fibers remove less plaque.
Don’t stop using the brush and dental floss if you have gingival bleeding. Use softer fabrics to prevent damage to your gums. If your gingival bleeding continues, visit your dentist.
Regularly visit your dentist for diagnosis and dental scaling. Inform your dentist if you are pregnant or suffer from diabetes, since in these conditions, the body resists gum disease with more difficulty.
It’s important no matter who you are, to check up on t your gums in the mirror every once in a while. Be mindful about your gum changing color or tissue. Visit your dentist immediately if you think you have periodontitis.
You can prevent gum disease by brushing and using dental floss twice a day.
Frequently asked questions about gum disease
Studies have shown that gum disease is caused due to an inflammatory reaction to bacteria in the gums, thus gum disease is not infectious. Still, the bacteria that cause the inflammatory reaction can be spread through saliva.
Gum disease may increase the risk of respiratory infections like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and pneumonia. Infections can be triggered by inhaling oral bacteria in your lungs and can probably lead to inflammation of your breathing airways.
If gum disease is not cured, the gingival tissue and the jawbone will be weakened. These both have dramatic effects, and will without a doubt affect the person’s day-to-day routine.
This disease is reversible in its early stages and usually withdraws with careful daily brushing and dental flossing. In more advanced stages of gum disease called periodontitis, the gums and bones that support the teeth are sternly damaged.
A person afflicted with gum disease will commonly have one or more of the following symptoms: swollen, bright red gums that bleed very easily even when brushing or flossing the teeth, bad taste or persistent bad breath, white spots or plaque on the gums.
Oftenly, such factors as poor brushing and the habit of dental flossing cause plaque to build up and get hard on the teeth. In advanced stages, gum disease may make gums bleed and cause problems like chewing painfully and even tooth loss.
Mouthwash is a solid choice to reduce plaque, keep the breath fresh, kill germs and bacteria that cause disease in the gums; it can even kill germs for up to 12 hours.
Gum disease can be diagnosed during regular dental checkups.
One way to help your gums to heal up is to wash them with saline solution. Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water. This solution soothes the irritated gum tissue and also helps eliminate infection in order to heal your gums.
The existing bacteria in gum disease can move in the body, and cause inflammation in the veins of the heart and infections in the heart valves, particularly in patients who suffer from heart problems.
In general, it is vital for children and teenagers to take good care of their oral health and keep their teeth and gums healthy in order to decrease the risk of gum disease in the future. Make sure your children brush their teeth twice a day and practice the right techniques of dental flossing. Moreover make sure you have regular dental checkups. Genetics can also play a significant role in the early development of gum disease.