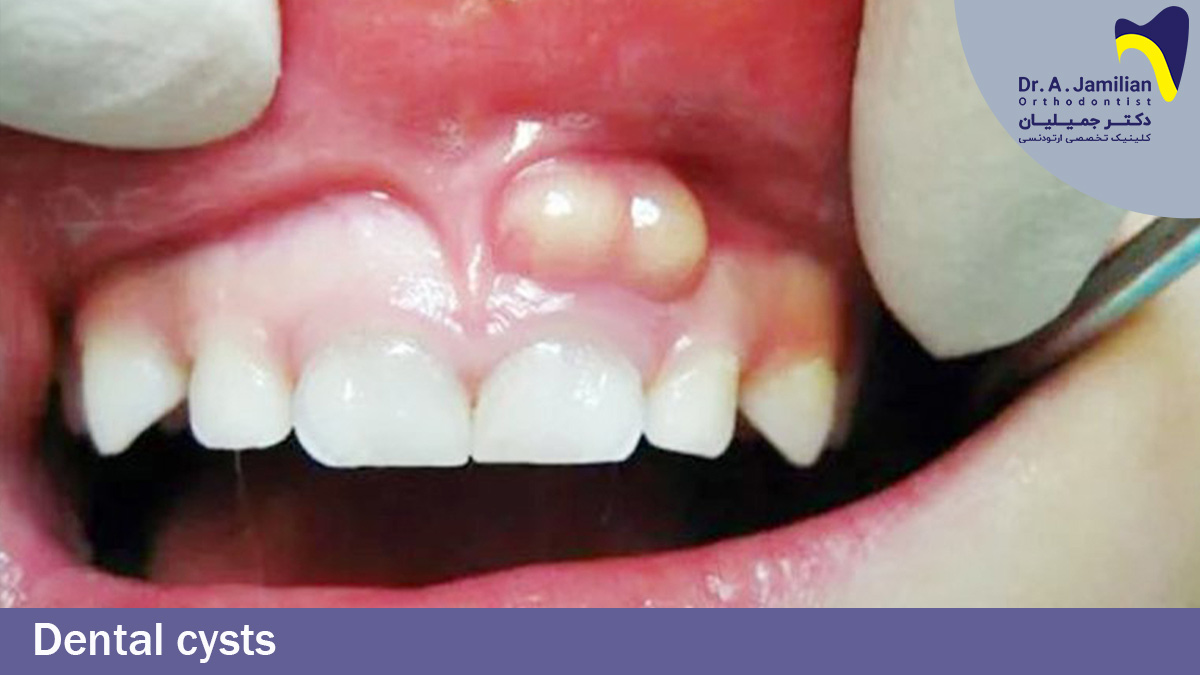
A problem that occurs frequently, is with infected teeth. Infected teeth are able to become a tooth abscess. It should be treated because in case it is not treated, it can change into a dental cyst. Dental cysts are able to affect the gums, jaw, and in some cases the face. On top of this, they are able to spread the infection to these parts. Immediately when noticing a dental cyst, patients should consult a qualified dentist in order to remove it. In the following parts, we will introduce different types of dental cysts, their side effects and how they can be treated.
What causes a dental cyst?
An infection which is completely bacterial and caused by severe decays and dental infection on the gums is called a dental cyst in dentistry.
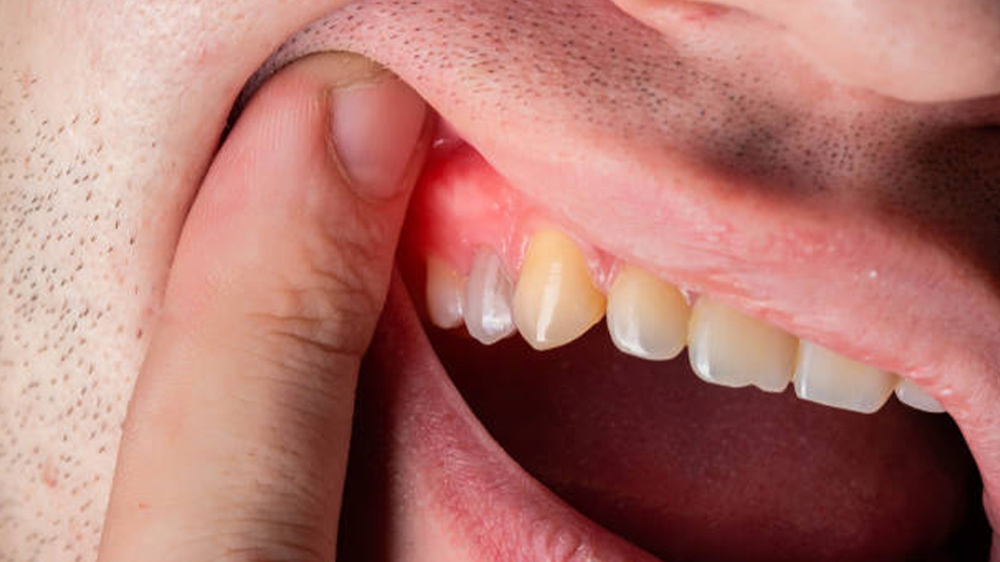
People with gingivitis are more likely to get this disease however, only 10% of them notice this disease and try to treat their dental cysts. Dental cysts, if left untreated, are able to affect the jawbone, gums and cause gingival cysts.
What are the complications of dental cysts?
One of the questions that dental cyst patients often ask themselves is what happens if the cyst is not treated and the side effects it may include. Here are a variety of the side effects of a dental cyst in case it is not treated:
- Dental cysts can cause severe pain in the patient’s mouth and teeth due to being infectious.
- Lack of a normal function of the teeth and gums.
- These cysts can put pressure on healthy teeth and the adjacent damaged teeth and then ruin them by the pressure that is caused as the result of infection and bacteria.
- If a dental cyst is formed on the jaw, it can erode and completely ruin the tooth by displacing the natural tissues of the gums and jaw.
- Because of being formed on the gums and at the end of the tooth root, dental cysts should be treated as soon as possible. In case of not being cured, they can put pressure on the teeth. Eventually, they result in the teeth getting loosened and fallen out.
- If dental cysts are not treated quickly after being diagnosed, when the patient is under nervous pressure, it can cause numbness in the patient’s face.
- Expansion of the jawbone is another side effect of a dental cyst which can be completely painless. However, it can frazzle the jawbone in the long run, and eventually will weaken the jaw.
Types of dental and gingival cysts
Here are five key sorts of dental and gingival cysts:
- Cysts that are noticed before a wisdom tooth often leads to the loss of the tooth bones and the destruction of adjacent teeth. Although, this problem will f often be solved by extracting the wisdom tooth.
- Vegetative cysts are another type of dental cysts that are formed before the formation of the main teeth. These cysts are often noticed in children when a tooth is passing through the jawbone and gingival tissue. These kinds of cysts are eliminated automatically after a tooth grows.
- Periapical cysts are the other types of dental and gingival cysts. They are commonly noticed around the root of the damaged tooth because of its infection. If the infection is not treated professionally and the patient only needs to take antibiotics, there is the possibility of a cyst’s formation. Thus, infected teeth must either be treated by a root canal or extracted in case the infection spreads and the root is lost.
- Pericardial cysts that aren’t completely eliminated after tooth extraction are known as residual cysts.
- Periodontal cysts are the most dangerous type of dental cysts, since they are often painless. Periodontal cysts are detected by X-ray, however, if they are not cured early, they can lead to the loss of the jawbone. These cysts are usually removed and treated with surgery.
How are dental cysts cured?
If the cyst is small, it is able to be treated with a root canal, however, massive dental cysts are often treated with surgery. The procedure is that the dentist first removes a small sample of the cyst for sampling. Then, it is the lab in order to determine the type of the dental cyst. Next and during one session, the dentist makes a small incision, so that the cyst is fully gone. In some cases, the dentist is not required to do a preoperative sampling.
Questions regarding dental cysts
In some cases, the dental cyst disappears without being treated, and in some cases, it’s treated by a root canal treatment. However, when the dental cyst gets infected, it is no longer a cyst and changes into a dental abscess. In these cases, the patient should not hesitate to see a dentist and treat it. Try to act immediately to drain and empty the infection. Dentists recommend that you take care of any sores or oddities in your mouth and teeth.
Different types of tumors, either benign or malignant, are able to appear in the mouth and jaw. Tumors and cysts in the jaw often have no type of symptoms. Benign tumors and tooth cysts may damage the bone and surrounding tissues. Dental cysts rarely lead to cancer on their own, but they can be one of the signs of cancer.
Dental cysts are removed by making a small incision on it and the remaining space is cleaned and dried. If the dental cyst is very large or causes damage to the mouth, the surgeon may also remove some parts of the tooth, the root of the tooth, or some part of the jaw.
Dental cysts may grow slowly for months or even years. However, sooner or later they get infected and possibly turn into a crisis. Which then, threatens the mouth and requires serious and immediate treatment.
A dental cyst is actually a sac that is not infectious and has been surrounded by distinct abnormal cells. However dental abscesses are full of pus and infection, commonly caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. The main difference between the symptoms of these two diseases is that: the dental cyst grows slowly and is often not painful unless it gets bigger, but abscesses appear suddenly and cause a lot of pain.