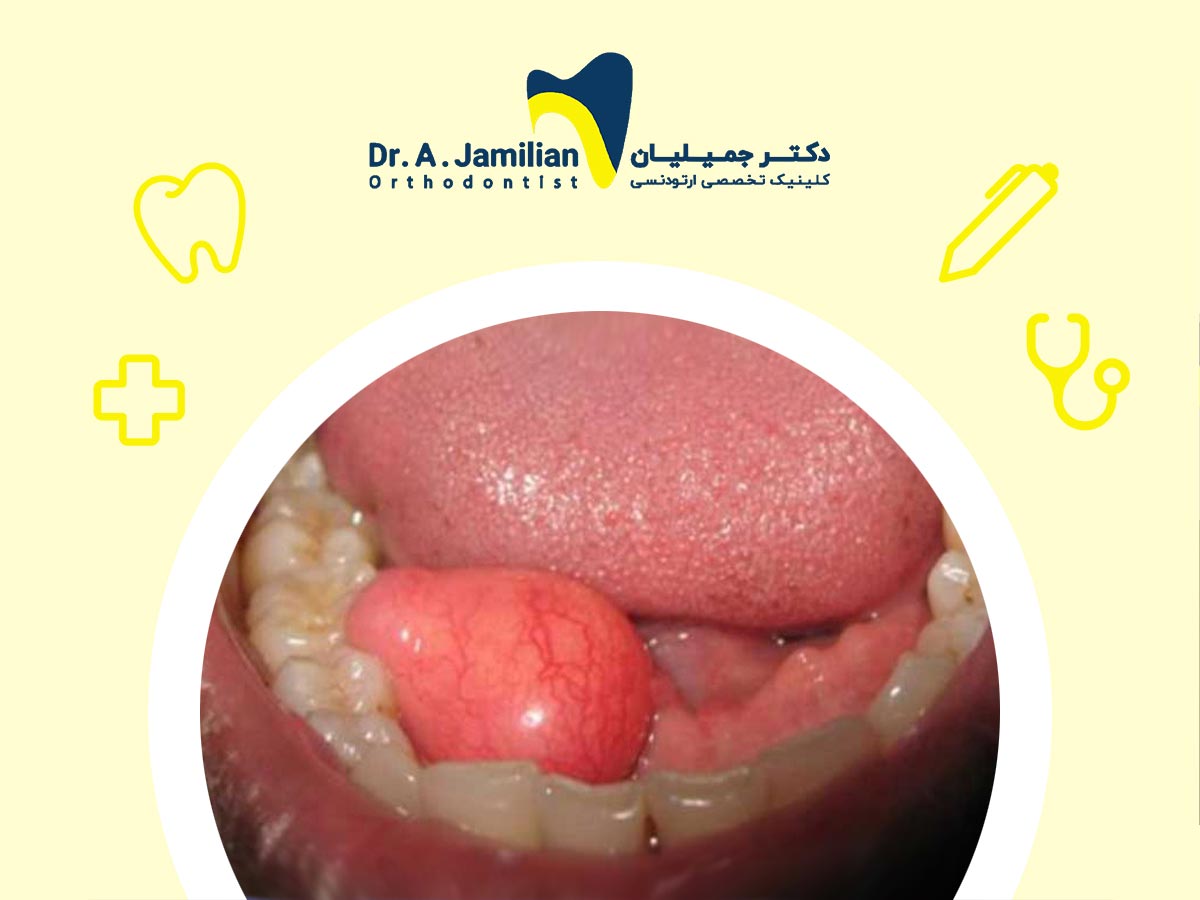
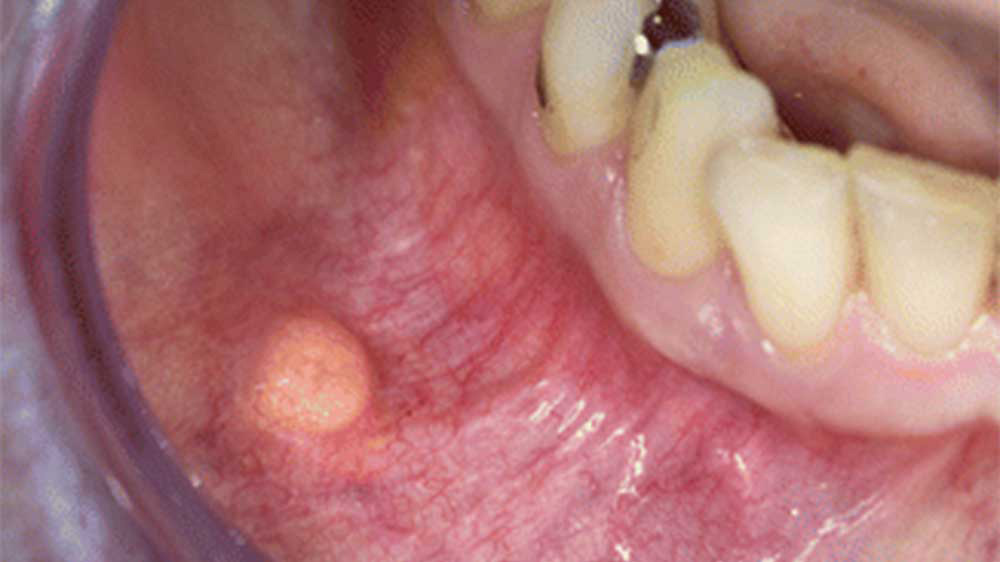
A lipoma refers to a round or oval-shaped lump of fatty tissue, which is usually found growing beneath skin. Lipoma actually is a disease of the fatty tissue in which fat lumps start to grow abnormally and after a while it feels like a protrusion. The lumps can grow across all parts of the body such as the waistline, shoulders and neck. However, they mostly are found across the upper part of the body and rarely are developed inside the oral cavity. In general, lipomas are considered as benign and non-carcinogenic lumps, which grow slowly. Generally, lipomas of the oral cavity are not common and prevalent, as studies show that only one tenth of people would develop it. Lipomas occur in middle ages (40-60 years old people). Most lipomas do not need any medical treatment; however, if they are found painful and annoying they can be removed very easily and with out-patient techniques.
However, in some cases lipoma is confused with liposarcomas, which are carcinogenic lumps of the fatty tissue, so it is suggested that in the case of having the mentioned symptoms, make sure to be examined by a specialist in order to be one hundred percent sure about it. In this article, we are going to make you familiar with the oral type of this disease.
Types of Lipomas
Before dealing with the lipoma of the oral cavity, it would be more helpful if we gained some information about its different forms and types. It helps you to reach a better understanding of lipoma. Depending on the fact that lumps are accompanied with other tissues, except the fatty tissue, lipomas have different forms. Fibrolipoma is an uncommon variant of lipoma whose tumors mostly contain fibrous tissues. If the tumor contains tiny blood veins it is called angiolipoma.
As one of the most challenging variants of lipomas, polymorphic is another variant of this disease containing big and colorful cells. It is most challenging because it usually is confused with liposarcoma, as the malignant and carcinogenic variant of this disease. Intramuscular variant is developed when the fatty lumps find their way into the mucosal muscles; it is usually found in the oral cavity, but it is very rare and uncommon.
Main Causes of Oral Cavity’s Lipoma
All of the causes of lipoma have not been identified yet. According to the specialists, it is a hereditary disorder which is inherited from parents into their children. Recent studies show that diabetes, HDL, obesity, senescence and some certain diseases are amongst the important causes of lipomas.
A number of diseases which can be effective in the development of lipoma are Dercum, Gardner syndrome, multiple lipomatosis and Madelung.
In dercum disease, also known as adiposis dolorosa or Anders disease, painful lipomas are developed across different parts of the body. Gardner syndrome is also a congenital disease, in which lipomas are developed across different parts of the body. Multiple lipomatosis, like Gardner syndrome, is a congenital disorder in which lipomas start to grow across different parts of the body including the oral cavity. People who consume high levels of alcohol would suffer from Madelung, in which lipomas grow in the mouth, neck and shoulders.
Symptoms of the Oral Cavity Lipomas
Lipoma is a sort of fatty tumor which is not painful; however, in cases where the fatty tumor is developed near the nerves and joints it would be painful. Thus, most people who have lipomas in their oral cavity or other parts of their body usually do not notice anything wrong.
The oral cavity’s lipoma is capsulated and is grown as a round or oval lump and does not spread into the adjacent tissues. Since the oral cavity’s lipoma is grown exactly beneath the outermost layer of the oral tissue, you can sense its movement, if you touch it. The diameter of the oral cavity’s lipomas is often less than 5 cm, however, in some cases we have seen oral cavity lipomas even with a 15 cm diameter.
This benign tumor mostly is seen in the facial mucosa, over tongue, lips and other parts of the oral cavity. The lumps are completely doughy and soft and mostly are visible. In cases where the tumor is superficial, its color is yellow, but the deep ones are pink.
Diagnosis of the Oral Cavity’s Lipoma
Oral cavity’s lipomas are diagnosed by specialist doctors or dentists. Diagnosis process usually begins with a simple physical examination in which the doctor or dentist diagnoses the type of tumor via touching the lump inside the oral cavity and asking questions about having pain in the area in question from the patient. Sometimes, to make sure about the non-carcinogenic nature of the tumor, your therapist would prescribe a biopsy from the lump for further tests and achieving a more precise diagnosis.
In some cases, it is possible that the lipoma is confused with a dental cyst during medical examinations. For this reason, in some cases for a more precise examination of lipoma, Ultrasound imaging or CT scan are prescribed. Given the patient’s condition, all of these techniques are used for differentiating oral lipoma from dental cysts, its locus and depth, its nature (benign or malignant) and how far it is intertwined with the nerves and blood veins. However, the first step for diagnosing an oral cavity’s lipoma is visiting a specialist doctor or dentist to get physical examinations.
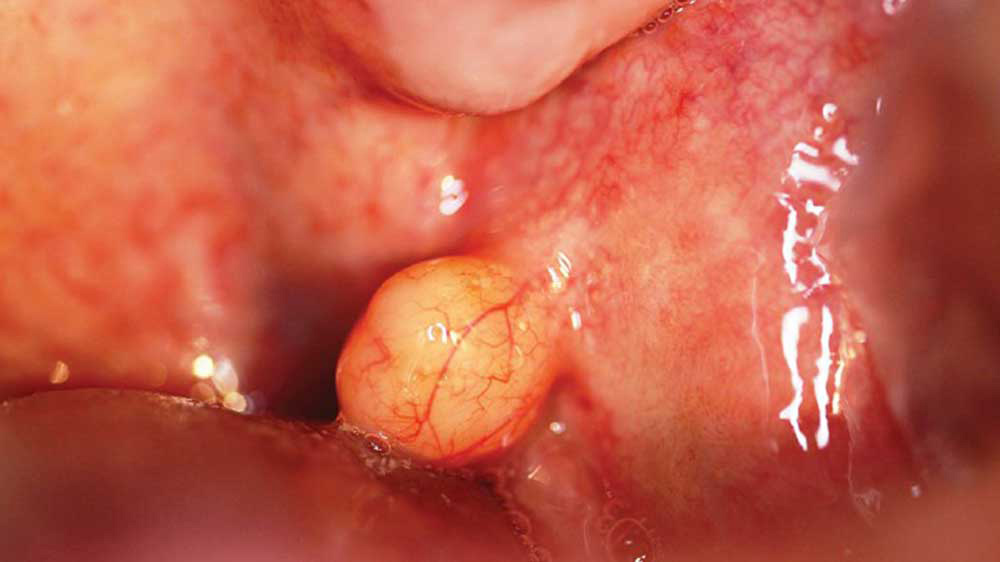
Treatment Techniques of Oral Cavity Lipoma
Oral cavity’s lipoma is a benign and relatively non hazardous disease, which is usually unpainful. When in reality, it is a small-sized lump. Thus, for years, people may live without being noticed about the presence of a lipoma in their mouth. However, without a doubt if a patient has pain or and/or more risky symptoms, they require treatment. In some scenarios, the tumor grows to an extent where chewing food or talking become difficulties; in such cases, more serious measures are required.
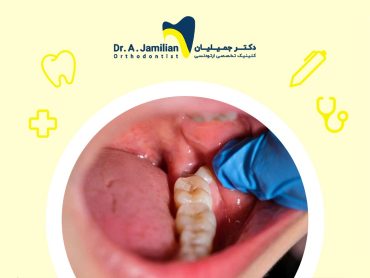
Treatment commonly is the local surgery of the tumor inside the oral cavity; in most cases the removed lumps do not recur. Its complete removal is more difficult, leading to a potential of its recurrence.
As well as surgery, liposuction can be an alternative treatment. Oral cavity’s lipoma can be removed using liposuction technique at the discretion of a dentist who is specialized in diagnosing oral and dental diseases. In this technique, a very thin and long needle is inserted into the lipoma and it removes the fatty tissue. Likewise, this technique prevents the recurrence of lipoma.
How to Prevent Oral Cavity’s Lipoma
As previously mentioned, both lipomas and its causes are mostly congenital and are inherited from parents to their children and these people are inclined to have lipomas in middle ages. Given this, it cannot be said that the disorder can be prevented completely, However, the possibility of having lipoma in the oral cavity can be minimized using useful foodstuff for oral health, avoiding alcoholic drinks and smoking.
Lipomas of the Oral Cavity FAQ
Oftenly, lipomas are considered as a common disorder, as 1 out of every 1000 people is affected by it.
Lipoma is a disorder occurring usually between ages of 40 and 60. As a result, it can be said that age plays a key and significant role in development of lipomas, however, finding lipomas in people younger or older than this age range is not impossible.
In general, lipomas develop in all people, apart from what their gender is. However, evidence shows that lipomas are more prevalent in women rather than men.
No, lipoma has a benign lump, so becoming a carcinogenic or risky tumor is very rare here. In most cases there is no need to be worried.
It is suggested to visit a dentist as soon as you feel a kind of lump or protrusion in your mouth.
Studies have shown that lipoma mostly are developed in facial mucosa and tongue, however, they have been found in other parts of the mouth.