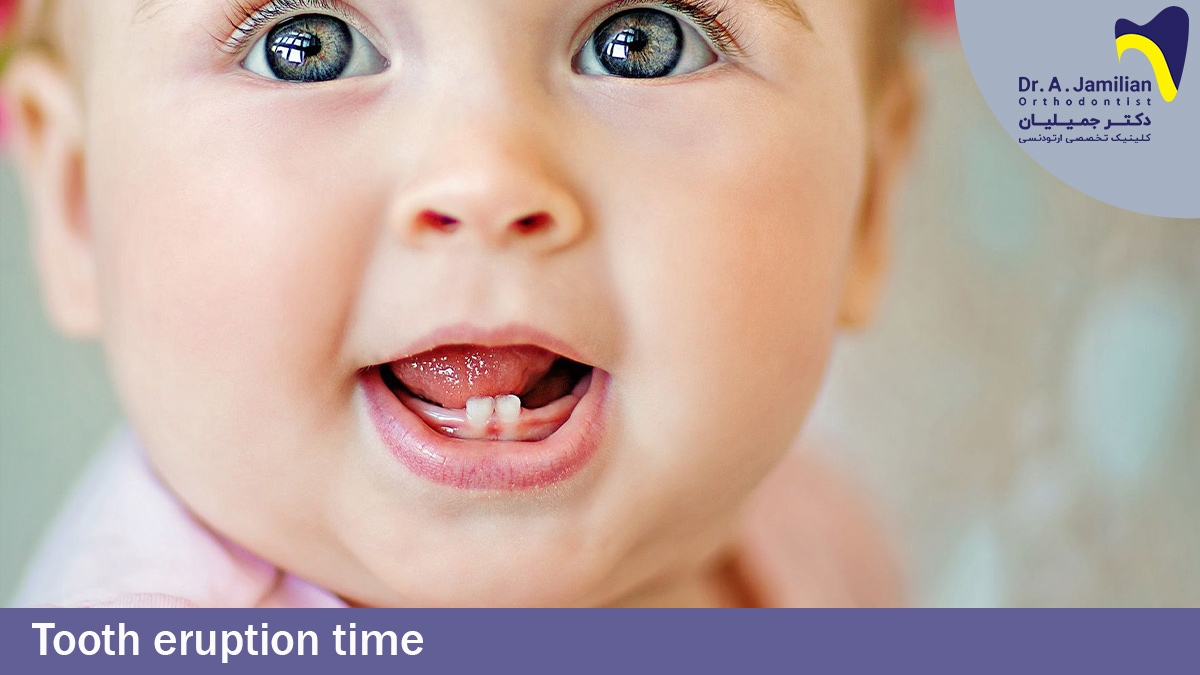
The eruption of the first milk teeth, i.e. two teeth in the middle of the mandible, starts when the child is around 6 months old. The natural time for eruption of milk teeth is between 5 to 7 months old. However, a kid’s teeth might grow sooner than the said time. For instance, when the child is one month old or the teeth might erupt later than the said time and when the child is 1.5 years old, which is normal.
Dental care during development of teeth
Commonly, the eruption of teeth requires no help or treatment. However, sometimes the child’s restlessness or crying might make their parents worried. The first sign of tooth eruption is the gradual redness of the gum at the place of growing the tooth. The child might become restless and sensitive. They put their hand or every object around them inside their mouth. Their saliva increases, they lose appetite and avoid eating food, cry a lot, and do not sleep. Sometimes they might have a mild fever. (Symptoms such as diarrhea are not considered as symptoms of tooth eruption since there is no scientific evidence to prove the relationship between these two phenomena). Massage the gum with a clean finger to calm the child.
Gentle massage of the gum or placing a cold metal like the back of a spoon can help soothe the child. You can wrap a small piece of ice in a clean cloth and place it on the inflamed gum. It should be performed with precision and caution. Sometimes the child might feel better by biting a piece of bread or a hard object. There are plastic rings specific to this problem, you can put them in the fridge and then let the child bite them.

Be careful to prevent the kid from swallowing these objects that can lead to choking. If the pain lasts, a dentist can subside the pain by prescribing medication. When the tooth has appeared in the mouth, all the pain and discomfort will go away.
A child approximately grows 4 teeth every 6 months and by the time the child is 3 years old, they will have 20 milk teeth, i.e. 10 teeth in the maxilla and 10 teeth in the mandible. However, this should be known without saying that every child is different. Or in other words, Some parents are concerned about the spaces between the milk teeth and ask whether it is normal or not, there is no need to worry about this issue. Since this space is normally seen between the posterior milk teeth in the maxilla and mandible.
Remember that the milk teeth of a baby are valuable since the child needs their milk teeth to be strong and healthy to be able to chew, talk, and have a beautiful appearance. The milk teeth are vital in the child’s chewing and nutrition during their growth age. Lacking the milk teeth can lead to malnutrition in the children, besides, lack of posterior milk teeth can cause a problem in the child’s speaking. Since the tongue must touch these teeth to be able to pronounce some words. Furthermore, milk teeth in children help preserve the required space for the permanent teeth.
Early fall of milk teeth
If your child lost their milk teeth before the proper time, take your kid to a dentist to preserve the place of the missing milk tooth with a tool called space maintainers. This tool does not allow the neighboring teeth to move to this place and maintain the space for the eruption of the permanent teeth. Otherwise, the neighboring milk teeth might move to the dental space and prevent the development of the permanent teeth and lead to crowded teeth in the child.
There are two types of space maintainers, removable and fixed. When your child is 5 years old, explain to them that losing the milk teeth is normal. It prevents them from getting upset when their teeth start to fall.
The eruption of the first permanent tooth
The first permanent tooth grows when the child is 6 or 7 years old, which is the mandibular first molar that is erupted behind the milk teeth. Over time, the other permanent teeth grow, and around the age of 11 to 13, all milk teeth have fallen and replaced with permanent teeth.
Most parents think that the first molar tooth that erupts behind the second milk tooth is actually a milk tooth since it is not replacing a milk tooth. However, it is not true and this tooth that erupted behind the milk teeth around the age of 6 or 7 is in fact a permanent tooth. Since the child does not care about their oral hygiene, most of the cases of dental caries are pertinent to this permanent tooth. Therefore, you should bear in mind that when the child is 6 or 7 years old, the last tooth that grows behind the milk teeth is their permanent tooth and they should care more about its health.
Relationship between milk & permanent teeth
There has been no report of a significant relationship between the milk and permanent teeth regarding their quality and resistance against caries, shape, etc. The child might have strong milk teeth without cavities while their permanent teeth are prone to decay and have decayed teeth, and vice versa.
Crooked permanent teeth
In most scenarios while the milk tooth has not fallen yet, the permanent tooth erupts and it becomes crooked. Often in films and tv shows we see crooked teeth as one of the worst teeth. Parent’s becoming worried is normal, and below will explain it. In the normal state of growth of the permanent teeth, the permanent tooth applies pressure to the root of the milk tooth and the root is gradually destroyed and when the milk tooth has lost its root completely, they fall out and the permanent tooth emerges. Sometimes the permanent tooth does not grow in its correct path and deviates from its path and the root of the milk tooth remains intact. Then, the permanent tooth emerges next to the milk tooth while the milk tooth is still in the mouth. This phenomenon is most common in the posterior mandibular milk teeth where the permanent teeth emerge behind them.
In this situation you should bear the following points in mind:
1-In case you notice the growth of a permanent tooth without losing the milk tooth, go to a dentist to extract the milk tooth.
2-If the tooth is crooked, in case of early detection and extraction of the milk tooth, the crooked tooth will move back to its place.
3-In case this disorder is not diagnosed in time and the permanent tooth is developed in the deviated path and reaches the surface of the opposite tooth and becomes fixed, extracting the milk tooth will not bring the permanent tooth back to its location and it should be treated through orthodontics treatment.
4-Paying regular visits to the dentist for the dental exams can help early diagnosis of a delay in the development of the permanent teeth and losing the milk teeth can help to prevent all of the above said malocclusions.






Im a huge fan already, man. Youve done a brilliant job making sure that people understand where youre arrival from. And let me tell you, I get it. huge stuff and I cant wait to read more of your information sites. What youve got to say is important and needs to be check out.
Thanks for your attention.
Thank you very much for your interesting text. I have been looking for such message for a really long time. Thank you.
.Hi. Thank you for your attention
your content is excellent and useful. It turns out that your work is unique it is clear from before and after orthodontic photos treatment.
. Hi.Thank you for your attention