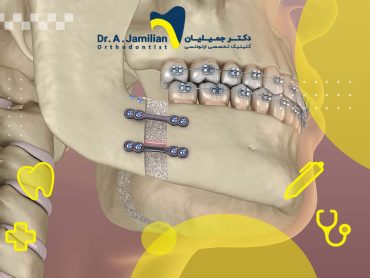
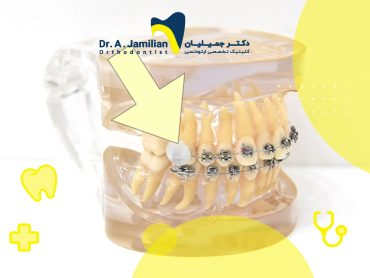
Beauty is an essential factor for people who want to undergo orthodontics. However, orthodontics cannot always modify the gums, and this problem is usually less considered as most patients are unaware of laser applications in orthodontics. Many orthodontists use the laser to increase and facilitate the effectiveness of orthodontic treatment. This advanced method can be used to achieve the best possible result in the shortest time, at the lowest cost, and with minimal pain and discomfort.
Orthodontic laser is specific to pigmented (colored) and soft tissues and is used in gingival surgeries. This type of laser cuts excess tissue with unparalleled precision, prevents bleeding, and disinfects the surgical site. Because of the laser’s high focus, the adjacent tissues are not damaged, no inflammation occurs, and the wound heals rapidly. The laser surgery is almost painless. The laser accelerates orthodontic treatment and provides more beautiful results.
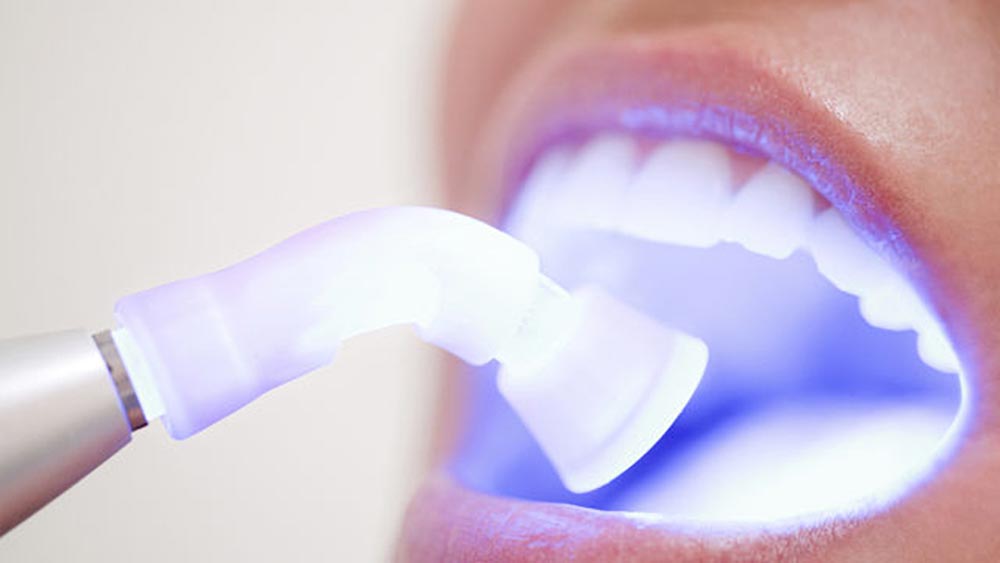
Laser performance and features
The laser features, such as power, wavelength, and timing, should be known to achieve favorable results. Laser therapy is a non-invasive and relatively quick method and is usually bleeding-free and painless. Observing safety measures is of crucial importance to prevent tissue damage during orthodontic surgery using the laser.
Dental lasers provide a very narrow pulse of a focused energy beam and precisely remove the target tissue. Some lasers are designed for hard tissue (teeth and bones) and some for soft tissue (gums). The best orthodontists can use soft tissue lasers instead of surgical blades in all operations to experience the least amount of pain and discomfort.
The laser used in orthodontics is specially designed for pigments, i.e., colored tissues. Soft tissue carbon dioxide laser or diode laser is commonly used for gingival surgeries. The laser accelerates orthodontics treatment and gives a more beautiful result. Since a very narrow laser beam is used at a particular wavelength, exact operations can be performed safely with a laser.
Laser applications in orthodontics
Laser has gained a significant place in orthodontics due to its advantages. Soft tissue lasers have several applications in gingival surgeries. Laser therapy reduces pain, bleeding, swelling, and wound shrinkage and increases accuracy. Low-intensity lasers can also control pain and accelerate tooth movement.
The laser emits a beam of focused energy and delivers a narrow pulse to the target tissue, leading to the separation of microscopic sections of gingival tissue. Patients who underwent laser gum surgery are always surprised by the comfort and painlessness of the treatment. The dentist uses an anesthetic gel to perform the treatment, and the main procedure takes only a few minutes. In orthodontics, the laser is generally used in the following cases:
- Shaping the gums to accelerate the orthodontic treatment process
- Accurately positioning the brackets by modifying the gums
- Attaching or detaching brackets
- Exposing the hidden tooth and its alignment through orthodontics, which required time-consuming and expensive surgery in the past
- Frenectomy or removing the excess frenum tissue that is sometimes too large and its rising results in an unpleasant condition
- Removing extra gums or solving the gingival smile when gums cover the maxillary teeth
Advantages of laser orthodontics
Laser therapy is the best option for easy treatment. Most areas can also be anesthetized with gel in laser surgery without any need for anesthetic injection. Concurrently with treatment, the laser also disinfects the area and reduces bleeding, swelling, or infection. The laser may affect the area like sunburn, which is resolved in less than a few days. In addition to speeding up and shortening the treatment, the laser increases the result’s durability. It is noteworthy that no adverse effects or contraindications for laser have been reported in surgical treatments so far.
- Faster and more effective treatment and shorter recovery time
- High safety
- Rapid recovery of the surgery site
- Laser incisions are very narrow, precise, and controlled
- Minimum pain
- Less invasion and no bleeding
- Reduced stress
- Blockage of lymphatic vessels, and hence reduced inflammation
- The laser can replace drilling for hard tissue removal
- Drilling may cause microscopic cracks on the teeth; however, laser eliminates the possibility of cracks.
- The laser helps bleach the teeth
- The chance to modify the gingival smile design
- Lightening the gums
- Modifying the enlargement and proper shaping of the gums
- Maintaining the oral health
Conclusion
The number of researchers and specialists interested in the application of laser in orthodontics is increasing every day. The literature on this field of dentistry indicates that laser will be extensively used in dental treatments in the near future. Along with specialists in various fields of medicine and dentistry, orthodontists take the numerous advantages of laser in the treatment process. When laser exposure protocols become more explicit in the near future, and the costs are reduced, the laser will play a significant role in orthodontics and reduce its costs.