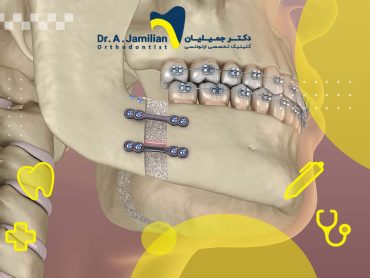
Orthodontics is a medical discipline dealing with changes in dental characteristics, related to the growth of teeth, hard tissue (jaws and teeth), and soft tissue (gums and other facial components) or a combination of the patient’s physical characteristics. Not to mention, it can substantially affect one’s general health.
Orthodontic treatments aim to strengthen positive dental characteristics and improve oral health. Orthodontic treatments begun in childhood can produce very favorable results for the child’s future, the most important of which is relieving the child of the need for complicated and advanced surgical procedures in adulthood.
Relationship between orthodontics and teeth growth in children
The relationship between orthodontics and tooth growth is of great importance reflecting the occurrence of changes during the growth and development of teeth and jaws. Some teeth may not have fully developed when children are taken to an orthodontist, and archwires will not be placed on such teeth.
In childhood, the development of the teeth and jaws isn’t finished getting in place and strengthening. The orthodontic treatment performed for children often consists of two main phases. The first phase includes removable orthodontics and is performed when both milk and permanent teeth exist in the child’s mouth and the maxilla has not been fully developed (the age of 7 to 12 years). Early orthodontic treatment may be performed for children to treat a developing malocclusion or to diagnose the imbalanced growth of jaws and facial bones. Here is exactly where the relationship between orthodontics and the development of jaws comes into effect, and removable orthodontic appliances are used to correct the position of jaws.
A comprehensive orthodontic treatment consisting of two phases is performed when most permanent teeth have erupted and the facial components are still growing during puberty (the age of 12 to 18 years depending on the individual development of each child). The second phase of the treatment helps the orthodontist ensure that each tooth is in its right position and in good alignment with lips, cheeks, tongue, and other teeth. This balance between facial components allows teeth to work together properly. After the first phase, the patient should use orthodontic brackets in Phase 2 for a short period.
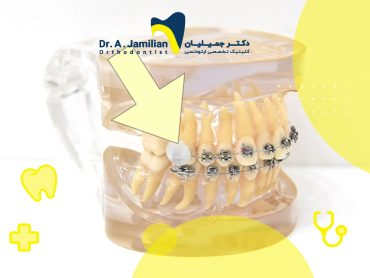
Children diagnosed with malocclusions should begin a procedure to correct the position of their jaws. Malocclusions inherited from parents to children can be treated by removable orthodontic appliances before puberty and the full development of jaws and teeth.
Relationship between orthodontics and the growth of jaws and teeth
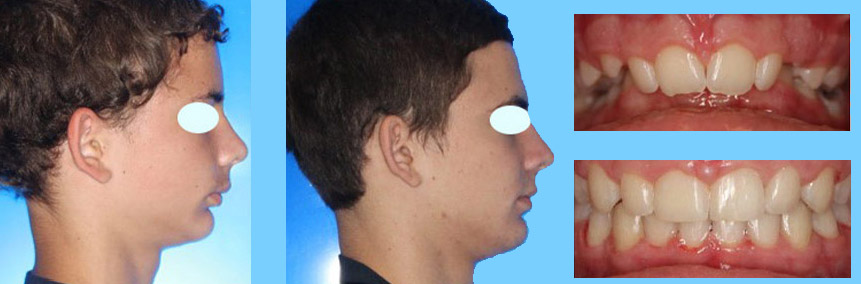
A major mandibular deformity in a child’s jaws is an easily treatable case by using orthodontic treatments. Such problems and malocclusions can be treated before puberty only by using orthodontic procedures. After puberty when the growth and development of jaws are completed, it is impossible to treat such problems only through orthodontics.
Orthodontic treatments should be followed by maxillofacial surgery to provide suitable conditions for jaws to be in their normal position. It is very difficult to move or change the structure of jaws after puberty.
Relationship between orthodontics and crooked teeth
In children with crooked teeth, orthodontic treatments can be applied to align fully developed teeth. Orthodontics offers the best treatment options to correct crooked and malpositioned teeth and improve the beauty of the smile design. It is noteworthy that an experienced orthodontist never places orthodontic archwires on less fully grown teeth.