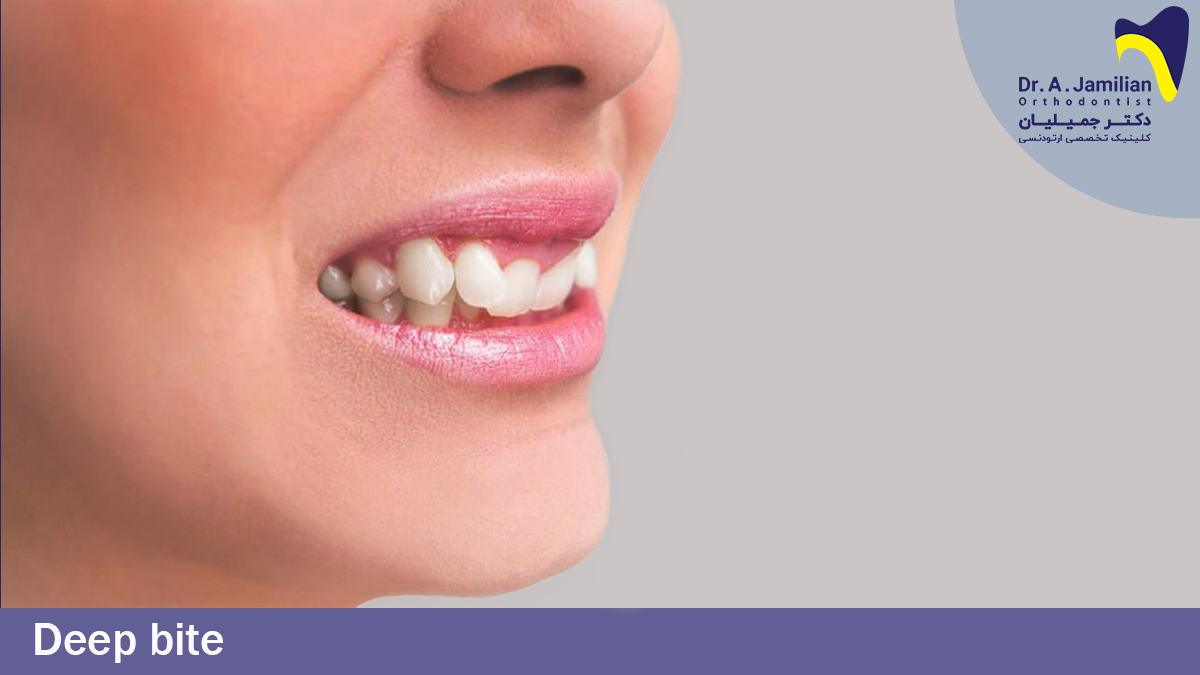
If everything’s alright the maxillary anterior teeth should vertically cover about 2 to 3 mm of the mandibular teeth. Deep bite refers to excessive coverage of the mandibular teeth by the maxillary anterior teeth, making the mandibular teeth appear less than normal. In some cases, the mandibular anterior teeth may contact and damage the maxillary soft tissue mucosa. Deep bite may have originated from impaired jaw development or inappropriate or excessive growth of the maxillary anterior teeth. Additionally, it may have a hereditary background.
Deep bite is one of the most harmful malformations threatening the teeth and jaws health. It may lead to teeth abrasion over time and greatly affects persons’ face and hence gradually decreases their smile beauty. In deep bite, the mandibular anterior teeth may affect the palate soft tissue and irritate the maxilla soft tissue.
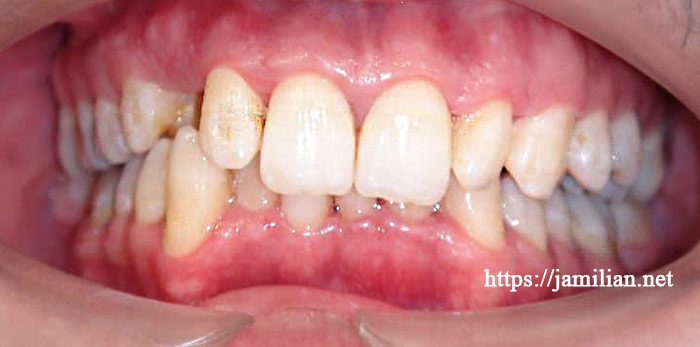
- Deep bite: front view
Untreated deep bite can result in gum damage in the lower front teeth (due to contact with the upper teeth masticatory edge), palate damage (due to the impact of the mandibular teeth masticatory edge on the palate) and premature abrasion of teeth or TMJ problems, leading to an unpleasant appearance. Therefore, early treatment of deep bite (before puberty) is of crucial importance. Deep bite can be easily treated with removable and fixed orthodontic appliances if the patient refers to a dentist before puberty, but maxillofacial surgery may be required if the patient visits at a higher age (after puberty).
Deep bite features
Deep bite symptoms are discussed in early and advanced stages. Unlike other jaw and tooth diseases which are often associated with an annoying pain, deep bite is known as a silent painless problem that progresses over time. Deep bite does not usually cause significant changes in the appearance of patients in the early stages. However, it may cause irreversible problems for patients and severely affect their beauty over time.
Deep bite: early stages
In the early stages of deep bite, the anterior teeth of the mandible are abraded and fine fractures are seen in the teeth along with gum swelling and bleeding. If the problem is not prevented, the upper edge of the mandibular and maxillary teeth will be severely abraded. In the early stages of deep bite, the teeth are abruptly scarred leading to gum bleeding, especially during brushing your teeth. Continuation of this process may lead to gingival recession over time due to penetration of the upper teeth into the gums and chewing of the gum tissue behind the maxillary teeth and the mandibular anterior teeth. Gradual development of this problem affects the individual’s appearance and smile and provides the basis for unseemly gums.
Deep bite: advanced stages
Deep bite progression results in severe tooth decay and pain in the affected teeth. It can often sensitize the teeth and sometimes result in TMJ pain in advanced scenarios.
Deep bite causes
Bite problems including deep bite, are caused by misalignment of the teeth and jaw, and often depend on genetics. Deep bite can be also attributed to teeth compression, irregularities and decay, overgrowth of the front teeth, inadequate growth of the back teeth, a combination of these two factors and inadequate growth of the jaw bones.
Deep bite effects
For many unspecialized people, the only problem with deep bite is its impact on personal beauty; however, it can result in more serious problems such as gum damage due to contact with the upper teeth masticatory edge, palate damage due to the impact of the mandibular teeth masticatory edge on the palate, general and premature abrasion of the teeth, gingival recession and bleeding, damage to the maxillary teeth roots, temporal problems and severe pain in these areas as well as esthetic problems. It is noteworthy that the severity of deep bite is exacerbated in adults who have lost their back teeth so that the affected people look older and with the involvement of the lower face.
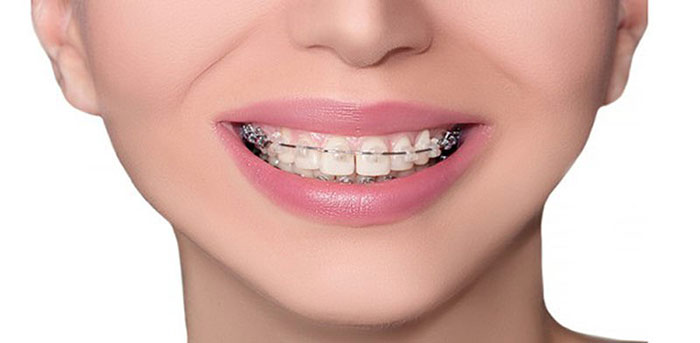
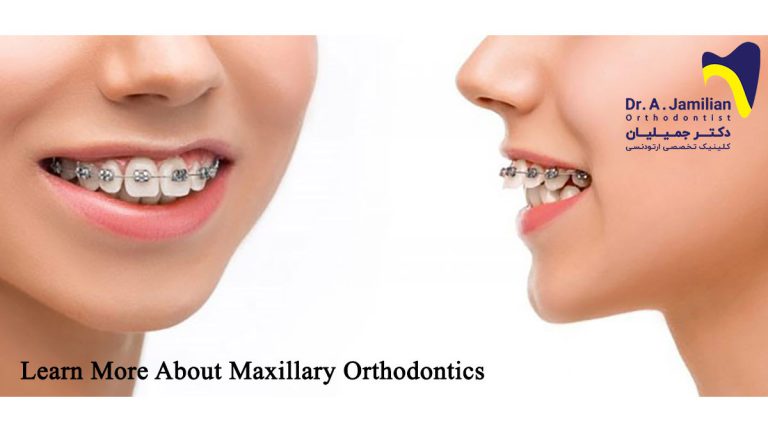
- Deep bite can be treated through orthodontics
Deep bite treatment
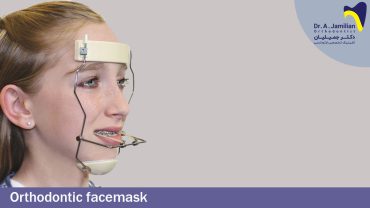
Maxillary and mandibular orthodontics and prosthetic reconstruction of the teeth damaged with the progression of deep bite are among the most important treatments recommended for those at early stages of deep bite. But advanced stages will not respond to these methods, and require more sophisticated treatments such as orthodontics and maxillofacial surgery.
Frequently asked questions regarding a deep bite
1-How is a deep bite treated?
Depending on the age of the patient and the severity of the deep bite, this problem can be solved with different treating methods. The main goal of this treatment is to align the teeth and jaws together. In most cases, more than one treatment is required in order to fix the problem. The first choice for treating a deep bite will often be the use of anterior bite block.
2-Is it possible for a deep bite to be genetic?
In most cases, genetics is of high significance in this regard. Genetic problems can play an influential role in the formation of deep bites.
3-How do I know if I have a deep bite?
Regular checkups will enable your dentist to diagnose and treat your problems as soon as possible. Then, if you do have it, he will refer you to an orthodontist. Such symptoms as chronic pain in the jaw, headaches, swallowing problems, having difficulty while speaking and chewing, chewing difficulty, suffering from tooth decay and sensitivity are often caused from deep bite.
4-Why does a deep bite need to be treated?
Treating a deep bite not only beautifies the smile form, but also will lead to important effects in treating such side effects as excessive tooth wear, damage to the maxillary mucosa made due to contact of the mandibular teeth with the maxilla, temporomandibular joint disorders, digestive problems, complete opening and closing of the mouth, speaking and even breathing.
5-What age is the most appropriate time to treat a deep bite?
A deep bite can be treated at any age. However, the treatment process will be much easier and more successful during childhood, because the flexibility of teeth and bones in childhood permits the orthodontist to apply the desired changes in the child’s mouth more effectively. Due to the hardening of bones, treating a deep bite in children over 12 years of age requires orthodontics with surgery. But, before the age of 12, a deep bite can be cured with orthodontics alone.
6-How long does the treatment of a deep Bite take?
A successful treatment of a deep bite usually takes about 1.5 to 2 years. However, this time can be different depending on the patient’s age, severity and nature of a deep bite.